Gleason Pattern 5 May Be a Prognostic Factor in Radium-223 Treatment
- PMID: 38962543
- PMCID: PMC11215439
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10345
Gleason Pattern 5 May Be a Prognostic Factor in Radium-223 Treatment
Abstract
Background/aim: Radium-223 treatment reduces the risk of death in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). This study analyzed the prognostic factors in patients treated with radium-223 dichloride.
Patients and methods: Patients who received radium-223 dichloride were retrospectively analyzed. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) decline rates were analyzed. Overall survival (OS) was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier curves, and prognostic factors for OS were assessed using Cox proportional hazards analysis.
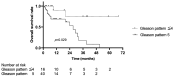
Results: Fifty-six patients were included in the study. The five-year OS rate in patients after diagnosis of CRPC was 62.2% [95% confidence interval (CI)=27.55-112.45], while the five-year OS rate in patients at the initiation of radium-223 treatment was 21.3% (95%CI=17.20-36.79). Six patients (11.1%) had a >50% PSA decline rate, and 10 (17.9%) had a >50% ALP decline rate. Cox proportional hazards analysis showed that PSA levels at the initiation of radium-223 treatment [hazard ratio (HR)=1.00; 95%CI=1.00-1.00; p=0.0054] and Gleason Pattern (GP) 5 (HR=5.42; 95%CI=1.08-27.27; p=0.0400) were associated with OS. Patients with GP 5 had a significantly poorer prognosis compared with patients with a GP ≤4. Early administration of radium-223 as a first- or second-line treatment was not associated with OS compared with late administration of radium-223 as a third-line or later treatment.
Conclusion: GP 5 and high PSA levels at radium-223 initiation were associated with worse OS. Radium-223 as first- or second-line treatment was not associated with OS. Therefore, a treatment strategy for CRPC based on GP 5 is needed.
Keywords: Gleason pattern; Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer; radium-223.
Copyright 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in relation to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An exploratory analysis of alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, and prostate-specific antigen dynamics in the phase 3 ALSYMPCA trial with radium-223.Ann Oncol. 2017 May 1;28(5):1090-1097. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx044. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28453701 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early alkaline phosphatase dynamics as biomarker of survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with radium-223.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Sep;48(10):3325-3334. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05283-6. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33686456 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Therapeutic Response to Radium-223 with an Automated Bone Scan Index among Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients: Data from Patients in the J-RAP-BSI Trial.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 16;15(10):2784. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102784. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345121 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of ECOG performance status and Gleason score in the survival of castration-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review.Asian J Androl. 2021 Mar-Apr;23(2):163-169. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_53_20. Asian J Androl. 2021. PMID: 33159024 Free PMC article.
-
Oncologic Response and Hospitalization Rate of Patients Receiving Cabazitaxel in the Fourth-Line and Beyond in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Analysis of a Retrospective Cohort and a Structured Literature Review.Urol Int. 2017;99(4):414-421. doi: 10.1159/000477943. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Urol Int. 2017. PMID: 28700990 Review.
References
-
- Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, Helle SI, O’Sullivan JM, Fosså SD, Chodacki A, Wiechno P, Logue J, Seke M, Widmark A, Johannessen DC, Hoskin P, Bottomley D, James ND, Solberg A, Syndikus I, Kliment J, Wedel S, Boehmer S, Dall’Oglio M, Franzén L, Coleman R, Vogelzang NJ, O’Bryan-Tear CG, Staudacher K, Garcia-Vargas J, Shan M, Bruland ØS, Sartor O, ALSYMPCA Investigators Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213–223. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1213755. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soloway MS, Hardeman SW, Hickey D, Todd B, Soloway S, Raymond J, Moinuddin M. Stratification of patients with metastatic prostate cancer based on extent of disease on initial bone scan. Cancer. 1988;61(1):195–202. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880101)61:1<195::aid-cncr2820610133>3.0.co;2-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- EMA restricts use of prostate cancer medicine XOFIGO. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/emarestricts-use-prostate-cancer-medic.... [Last accessed on January 14, 2022]
-
- Bauckneht M, Rebuzzi SE, Signori A, Frantellizzi V, Murianni V, Lodi Rizzini E, Mascia M, Lavelli V, Donegani MI, Ponzano M, Gaudiano A, Stazza ML, Licari M, Cavallini L, Laghi V, Cindolo L, Maggi M, Sciarra A, Mammucci P, Sambuceti G, Costa RP, Spanu A, Rubini G, Monari F, De Vincentis G, Fornarini G. The prognostic power of inflammatory indices and clinical factors in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with radium-223 (BIO-Ra study) Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49(3):1063–1074. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05550-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous