The research landscape of ferroptosis in neurodegenerative disease: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38962561
- PMCID: PMC11221830
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1417989
The research landscape of ferroptosis in neurodegenerative disease: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Ferroptosis, a newly proposed concept of programmed cell death, has garnered significant attention in research across different diseases in the last decade. Despite thorough citation analyses in neuroscience, there is a scarcity of information on ferroptosis research specifically related to neurodegenerative diseases.
Method: The Web of Science Core Collection database retrieved relevant articles and reviews. Data on publications, countries, institutions, authors, journals, citations, and keywords in the included studies were systematically analyzed using Microsoft Excel 2019 and CiteSpace 6.2.R7 software.
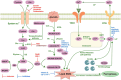
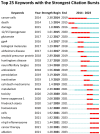
Result: A comprehensive analysis and visualization of 563 research papers on ferroptosis in neurodegenerative diseases from 2014 to 2023 revealed emerging research hotspots and trends. The number of annual publications in this field of study has displayed a pattern of stabilization in the early years of the decade, followed by a notable increase in the later years and peaking in 2023 with 196 publications. Regarding publication volume and total citations, notable research contributions were observed from countries, institutions, and authors in North America, Western Europe, and China. Current research endeavors primarily focus on understanding the intervention mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases through the ferroptosis pathway and exploring and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
Conclusion: The study highlights key areas of interest and emerging trends in ferroptosis research on neurodegenerative diseases, offering valuable insights for further exploration and potential directions for diagnosing and treating such conditions.
Keywords: CiteSpace; bibliometric analysis; ferroptosis; hotspots; knowledge graph; neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Feng, Shui, Wang, Yu, Liu and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The landscape of research on ferroptosis under hypoxic conditions: a bibliometric analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1519000. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1519000. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40206079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric study and visualization analysis of ferroptosis-inducing cancer therapy.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 9;9(9):e19801. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19801. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809417 Free PMC article.
-
The Research Landscape of Ferroptosis in Cancer: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 25;10:841724. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.841724. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35693942 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge mapping of ferroptosis in Parkinson's disease: a bibliometric analysis: 2012-2023.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Aug 30;16:1433325. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1433325. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39280701 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of ferroptosis in tumor resistance: development and emerging trends.Front Immunol. 2025 May 9;16:1580222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1580222. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40416987 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gait analysis in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a bibliometric analysis of global trends, hotspots, and emerging frontiers.Front Aging. 2025 Jun 19;6:1592464. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1592464. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40612530 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

