A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Role of Bempedoic Acid in Cardiovascular Outcomes for Patients With Statin Intolerance
- PMID: 38962583
- PMCID: PMC11221203
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61572
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Role of Bempedoic Acid in Cardiovascular Outcomes for Patients With Statin Intolerance
Abstract
Atherosclerosis, a multifaceted pathogenic process affecting the arteries and aorta, poses a significant threat because of its potential to impede or entirely obstruct blood flow by narrowing blood vessels. This intricate progression involves various factors such as dyslipidemia, immunological responses, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. The initial phase manifests as the formation of fatty streaks, considered a pivotal hallmark in the inception of atherosclerotic plaques, a process that can commence as early as childhood. Over time, this process evolves, characterized by the thickening of the arterial inner layer (intima) and accumulation of lipid-laden macrophages, commonly known as foam cells, along with the buildup of the extracellular matrix. Subsequent stages witness the proliferation and aggregation of smooth muscle cells, culminating in the formation of atheroma plaques. As these lesions progress, apoptosis can occur in the deeper layers, further recruiting macrophages, which may undergo calcification and transform into atherosclerotic plaques. Notably, mechanisms such as arterial remodeling and intraplaque hemorrhage also contribute significantly to the progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, although these facets fall beyond the scope of this article. This study aimed to systematically review and conduct a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials investigating the efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid in statin-intolerant patients with hyperlipidemia and to provide conclusions and recommendations accordingly. A systematic search of databases, such as PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase, will be performed. Only randomized trials will be included comparing bempedoic acid with placebo in statin-intolerant patients. This study aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of bempedoic acid in managing hyperlipidemia in statin-intolerant patients. In primary prevention, for patients unable to tolerate recommended statins, bempedoic acid was associated with a significant reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) as the primary endpoint.
Keywords: " "atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; adverse cardiovascular outcomes; bempedoic acid; cardiovascular disease prevention; cardiovascular disease risk factor; high-statin therapy; hyperuricemia. dyslipidemia. bmi .fbs . cardiovascular risk; pattern of dyslipidemia; statin intolerance; statin use.
Copyright © 2024, Serour et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
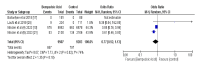


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid added to ezetimibe in statin-intolerant patients with hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, placebo-controlled study.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Oct;277:195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 29910030 Clinical Trial.
-
Rationale and design of the CLEAR-outcomes trial: Evaluating the effect of bempedoic acid on cardiovascular events in patients with statin intolerance.Am Heart J. 2021 May;235:104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2020.10.060. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Am Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33470195 Clinical Trial.
-
Bempedoic Acid: Lipid Lowering for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention.Heart Int. 2023 Nov 1;17(2):27-34. doi: 10.17925/HI.2023.17.2.1. eCollection 2023. Heart Int. 2023. PMID: 38419721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular events in patients treated with bempedoic acid vs. placebo: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2023 Sep 20;9(6):583-591. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvad052. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37463824
-
Bempedoic Acid can Reduce Cardiovascular Events in Combination with Statins or As Monotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2023 Nov;23(6):695-708. doi: 10.1007/s40256-023-00606-4. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37672202
Cited by
-
The effect of bempedoic acid on histopathologic changes associated with natural aging in rat lungs.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03608-x. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40155848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olvera Lopez E, Ballard BD, Jan A. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls ; 2024. Cardiovascular Disease. - PubMed
-
- ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Reiner Z, Catapano AL, De Backer G, et al. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1769–1818. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
