Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Associated With Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 38962633
- PMCID: PMC11221388
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61557
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Associated With Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
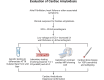
Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) involves the abnormal deposition and accumulation of amyloid proteins in the heart muscle. A hallmark of disease progression is declining heart function, which can lead to structural irregularities, arrhythmias, and ultimately heart failure. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia that presents in CA patients, and this arrhythmia is significant because it can moderately increase the risk of patients developing intracardiac thrombi, thereby putting them at risk for thromboembolic events. The management of this complication entails the use of anticoagulants like vitamin K antagonists and direct oral anticoagulants to reduce the risk of thrombus formation. This article seeks to review AF in CA and the use of anticoagulation therapy for the management and reduction of thromboembolic risk. The major conclusions of this review are centered around the need for safe administration of anticoagulant therapy to CA patients, regardless of their CHA2DS2-VASc risk score. This review highlights the importance of taking a multidisciplinary or collaborative approach to CA treatment to ensure that all aspects of this multifaceted disease can be properly managed while minimizing adverse events like bleeding risk and drug-drug interactions.
Keywords: amyloidosis al; anticoagul; atrial fibrillation (af); atrial fibrillation cardiac amyloidosis; attr amyloidosis.
Copyright © 2024, Monga et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atrial fibrillation in the setting of cardiac amyloidosis - A review of the literature.J Cardiol. 2024 Sep;84(3):155-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2024.03.008. Epub 2024 Mar 31. J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38565394 Review.
-
Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation and Intervention Therapy in Cardiac Amyloidosis.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 May 22;26(5):37064. doi: 10.31083/RCM37064. eCollection 2025 May. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40475717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atrial Fibrillation, Thromboembolic Risk, and Anticoagulation in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Review.J Card Fail. 2023 Jan;29(1):76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2022.08.008. Epub 2022 Sep 17. J Card Fail. 2023. PMID: 36122817 Review.
-
[A comparison of CAS risk model and CHA2DS2-VASc risk model in guiding anticoagulation treatment in Chinese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2022 Sep 24;50(9):888-894. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20210826-00740. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36096706 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Stroke Risk Stratification Schemes in Atrial Fibrillation in the Era of Non- Vitamin K Anticoagulants: Misleading and Obsolete, At Least for the "Low-Risk" Patients?Curr Drug Targets. 2017 Nov 30;18(16):1852-1865. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160905111822. Curr Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 27593686 Review.
Cited by
-
A Response to: Letter to the Editor Regarding "Tafamidis 61 mg Patient Characteristics and Persistency? A Retrospective Analysis of German Statutory Health Insurance Data (IQVIA™ LRx)".Cardiol Ther. 2024 Dec;13(4):815-817. doi: 10.1007/s40119-024-00383-4. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Cardiol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39441480 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Current landscape of clinical management for systemic light chain amyloidosis.Future Cardiol. 2025 Mar;21(4):203-205. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2025.2460392. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Future Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39885778 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis as a cause of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. González-López E, Gallego-Delgado M, Guzzo-Merello G, et al. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:2585–2594. - PubMed
-
- Atrial fibrillation in the setting of cardiac amyloidosis - a review of the literature. Bazoukis G, Saplaouras A, Efthymiou P, et al. J Cardiol. 2024 - PubMed
-
- Management of arrhythmias in cardiac amyloidosis. Giancaterino S, Urey MA, Darden D, Hsu JC. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6:351–361. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
