Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Bibliometric Analysis Using the Scopus Database
- PMID: 38962641
- PMCID: PMC11221973
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61613
Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Bibliometric Analysis Using the Scopus Database
Abstract
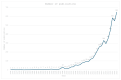
Primary joint replacements are performed increasingly often worldwide, driven by an aging population, improvement in surgical techniques, and advancements in implant designs. While more attention has traditionally been focused on weight-bearing joints such as the hip and knee, shoulder replacement surgeries have gained increasing attention in recent years due to the population's demand for a better quality of life. Thus far, a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of shoulder arthroplasty-related publications using the Scopus database has not yet been conducted. This bibliometric analysis aims to fill this gap by reviewing the Scopus database from its inception until 2023 to examine the literature on shoulder arthroplasty. A total of 5300 publications meeting the selection criteria were included in this analysis. The turn of the century marked a significant turning point for the field of shoulder arthroplasty, with an increasing number of publications produced annually. This trend can be attributed to the improvement of implant designs, which have become more consistent and reliable over time. While the majority of articles were authored by researchers and clinicians from the United States of America (USA), publications by French authors had a higher scholarly impact in the field. There is a noticeable gap in research on shoulder arthroplasty in developing countries, possibly due to the prohibitively high cost of implants and the prioritization of other healthcare sectors. This bibliometric analysis, utilizing Scopus data, serves as a guiding light for researchers, clinicians, and policymakers, potentially fostering collaborative projects and guiding the development of future studies to further advance the field of shoulder arthroplasty, particularly in developing countries.
Keywords: anatomical hemi shoulder arthroplasty; bibliometric analyis; research trend; reverse shoulder arthroplasty; shoulder arthroplasty/ replacement; total shoulder arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2024, Nizam Siron et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Shoulder replacement for osteoarthritis: a review of surgical management. Pandya J, Johnson T, Low AK. Maturitas. 2018;108:71–76. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous