Metabolic signatures and risk of sarcopenia in suburb-dwelling older individuals by LC-MS-based untargeted metabonomics
- PMID: 38962681
- PMCID: PMC11220188
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1308841
Metabolic signatures and risk of sarcopenia in suburb-dwelling older individuals by LC-MS-based untargeted metabonomics
Abstract
Background: Untargeted metabonomics has provided new insight into the pathogenesis of sarcopenia. In this study, we explored plasma metabolic signatures linked to a heightened risk of sarcopenia in a cohort study by LC-MS-based untargeted metabonomics.
Methods: In this nested case-control study from the Adult Physical Fitness and Health Cohort Study (APFHCS), we collected blood plasma samples from 30 new-onset sarcopenia subjects (mean age 73.2 ± 5.6 years) and 30 healthy controls (mean age 74.2 ± 4.6 years) matched by age, sex, BMI, lifestyle, and comorbidities. An untargeted metabolomics methodology was employed to discern the metabolomic profile alterations present in individuals exhibiting newly diagnosed sarcopenia.
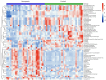
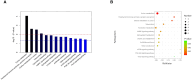
Results: In comparing individuals with new-onset sarcopenia to normal controls, a comprehensive analysis using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) identified a total of 62 metabolites, predominantly comprising lipids, lipid-like molecules, organic acids, and derivatives. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis indicated that the three metabolites hypoxanthine (AUC=0.819, 95% CI=0.711-0.927), L-2-amino-3-oxobutanoic acid (AUC=0.733, 95% CI=0.598-0.868) and PC(14:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (AUC= 0.717, 95% CI=0.587-0.846) had the highest areas under the curve. Then, these significant metabolites were observed to be notably enriched in four distinct metabolic pathways, namely, "purine metabolism"; "parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action"; "choline metabolism in cancer"; and "tuberculosis".
Conclusion: The current investigation elucidates the metabolic perturbations observed in individuals diagnosed with sarcopenia. The identified metabolites hold promise as potential biomarkers, offering avenues for exploring the underlying pathological mechanisms associated with sarcopenia.
Keywords: Chinese; LC-MS; risk; sarcopenia; untargeted metabonomics.
Copyright © 2024 Han, Chen, Liang, Liu, Yu, Song, Zhao, Zhang, Zhu, Shi and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metabolic signatures and potential biomarkers of sarcopenia in suburb-dwelling older Chinese: based on untargeted GC-MS and LC-MS.Skelet Muscle. 2024 Mar 7;14(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13395-024-00337-3. Skelet Muscle. 2024. PMID: 38454497 Free PMC article.
-
Study on plasma metabolomics profiling of depression in Chinese community-dwelling older adults based on untargeted LC/GC‒MS.Sci Rep. 2024 May 5;14(1):10303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60836-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38705886 Free PMC article.
-
Novel metabolic and lipidomic biomarkers of sarcopenia.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Oct;15(5):2175-2186. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13567. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. PMID: 39169398 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric based approaches in urine metabolomics and biomarker discovery.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2017 Mar;36(2):115-134. doi: 10.1002/mas.21455. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2017. PMID: 25881008 Review.
-
Challenges and emergent solutions for LC-MS/MS based untargeted metabolomics in diseases.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018 Nov;37(6):772-792. doi: 10.1002/mas.21562. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018. PMID: 29486047 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of the cardiometabolic index with sarcopenia among U.S. adults: NHANES 2011-2018 findings.PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0323905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323905. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40373017 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Precision in Sarcopenia Assessment: The Challenges of Multimodal Data Analysis in the Era of AI.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 7;26(9):4428. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094428. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nontargeted and targeted metabolic profile of metabolic syndrome patients: a study based on Yi and Han populations in Yunnan.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 14;16:1488099. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1488099. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40438394 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes and Sarcopenia: Metabolomic Signature of Pathogenic Pathways and Targeted Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 5;26(15):7574. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157574. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ, Bhasin S, Morley JE, Newman AB, et al. . Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med Directors Assoc. (2011) 12:249–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2011.01.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

