Lysophosphatidylcholine binds α-synuclein and prevents its pathological aggregation
- PMID: 38962715
- PMCID: PMC11221426
- DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwae182
Lysophosphatidylcholine binds α-synuclein and prevents its pathological aggregation
Abstract
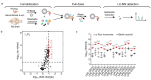
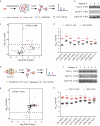
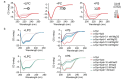
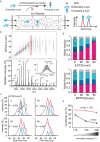
Accumulation of aggregated α-synuclein (α-syn) in Lewy bodies is the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD). Genetic mutations in lipid metabolism are causative for a subset of patients with Parkinsonism. The role of α-syn's lipid interactions in its function and aggregation is recognized, yet the specific lipids involved and how lipid metabolism issues trigger α-syn aggregation and neurodegeneration remain unclear. Here, we found that α-syn shows a preference for binding to lysophospholipids (LPLs), particularly targeting lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) without relying on electrostatic interactions. LPC is capable of maintaining α-syn in a compact conformation, significantly reducing its propensity to aggregate both in vitro and within cellular environments. Conversely, a reduction in the production of cellular LPLs is associated with an increase in α-syn accumulation. Our work underscores the critical role of LPLs in preserving the natural conformation of α-syn to inhibit improper aggregation, and establishes a potential connection between lipid metabolic dysfunction and α-syn aggregation in PD.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; lysophosphatidylcholine, aggregation; α-synuclein.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
