Applications and advances in molecular diagnostics: revolutionizing non-tuberculous mycobacteria species and subspecies identification
- PMID: 38962772
- PMCID: PMC11220129
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1410672
Applications and advances in molecular diagnostics: revolutionizing non-tuberculous mycobacteria species and subspecies identification
Abstract
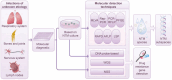
Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infections pose a significant public health challenge worldwide, affecting individuals across a wide spectrum of immune statuses. Recent epidemiological studies indicate rising incidence rates in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent populations, underscoring the need for enhanced diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. NTM infections often present with symptoms similar to those of tuberculosis, yet with less specificity, increasing the risk of misdiagnosis and potentially adverse outcomes for patients. Consequently, rapid and accurate identification of the pathogen is crucial for precise diagnosis and treatment. Traditional detection methods, notably microbiological culture, are hampered by lengthy incubation periods and a limited capacity to differentiate closely related NTM subtypes, thereby delaying diagnosis and the initiation of targeted therapies. Emerging diagnostic technologies offer new possibilities for the swift detection and accurate identification of NTM infections, playing a critical role in early diagnosis and providing more accurate and comprehensive information. This review delineates the current molecular methodologies for NTM species and subspecies identification. We critically assess the limitations and challenges inherent in these technologies for diagnosing NTM and explore potential future directions for their advancement. It aims to provide valuable insights into advancing the application of molecular diagnostic techniques in NTM infection identification.
Keywords: drug resistance gene; molecular diagnostics; next-generation sequencing; non-tuberculous mycobacterium; whole genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Tang, Li, Xu, Ao and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cowman S, Wilson R, Loebinger MR. Opportunistic mycobacterial diseases. Medicine. (2016) 44:390–2. doi: 10.1016/j.mpmed.2016.03.010 - DOI
-
- Furuuchi K, Morimoto K, Yoshiyama T, Tanaka Y, Fujiwara K, Okumura M, et al. . Interrelational changes in the epidemiology and clinical features of nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease and tuberculosis in a referral hospital in Japan. Respir Med. (2019) 152:74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2019.05.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

