Interrelated involvement of the endocannabinoid/endovanilloid (TRPV1) systems and epigenetic processes in anxiety- and working memory impairment-related behavioural effects of nicotine as a stressor
- PMID: 38963015
- PMCID: PMC11222983
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13421
Interrelated involvement of the endocannabinoid/endovanilloid (TRPV1) systems and epigenetic processes in anxiety- and working memory impairment-related behavioural effects of nicotine as a stressor
Abstract
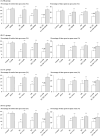
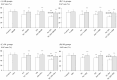
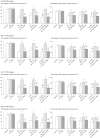
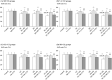
The addictive use of nicotine contained in tobacco is associated with stressor-like emotional and cognitive effects such as anxiety and working memory impairment, and the involvement of epigenetic mechanisms such as histone acetylation has recently been reported. Although the precise nature of behavioural plasticity remains unclear, both anxiogenic- and working memory impairment-like effects were observed in the present experimental model of mice treated with repeated subcutaneous nicotine and/or immobilization stress, and these effects were commonly attenuated by the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors that induce histone acetylation. Such HDAC inhibitor-induced resilience was mimicked by ligands for the endocannabinoid (ECB) system, a neurotransmitter system that is closely associated with nicotine-induced addiction-related behaviours: the anxiogenic-like effects were mitigated by the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) agonist arachidonylcyclopropylamide (ACPA), whereas the working memory impairment-like effects were mitigated by the CB1 antagonist SR 141716A. Moreover, the effects of the HDAC inhibitors were also mimicked by ligands for the endovanilloid (transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 [TRPV1]) system, a system that shares common characteristics with the ECB system: the anxiogenic-like effects were mitigated by the TRPV1 antagonist capsazepine, whereas the working memory impairment-like effects were mitigated by the TRPV1 agonist olvanil. Notably, the HDAC inhibitor-induced anxiolytic-like effects were attenuated by SR 141716A, which were further counteracted by capsazepine, whereas the working memory improvement-like effects were attenuated by capsazepine, which were further counteracted by SR 141716A. These results suggest the contribution of interrelated control of the ECB/TRPV1 systems and epigenetic processes such as histone acetylation to novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: anxiety/working memory; endocannabinoid; endovanilloid (TRPV1); epigenetic histone acetylation; nicotine; stress.
© 2024 The Author(s). Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no competing interests to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Putative Epigenetic Involvement of the Endocannabinoid System in Anxiety- and Depression-Related Behaviors Caused by Nicotine as a Stressor.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 12;11(7):e0158950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158950. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27404492 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of TRPV1 receptor ligands against nicotine-induced depression-like behaviors.BMC Pharmacol. 2011 Jul 18;11:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-11-6. BMC Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21767384 Free PMC article.
-
Working memory- and anxiety-related behavioral effects of repeated nicotine as a stressor: the role of cannabinoid receptors.BMC Neurosci. 2013 Feb 9;14:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-14-20. BMC Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23394117 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms associated with addiction-related behavioural effects of nicotine and/or cocaine: implication of the endocannabinoid system.Behav Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;28(7):493-511. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000326. Behav Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28704272 Review.
-
The endocannabinoid system as a target for novel anxiolytic drugs.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017 May;76(Pt A):56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.12.033. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017. PMID: 28434588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic . 2019. 2019. Accessed June 3, 2024. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1239531/retrieve
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic . 2021. 2021. Accessed June 3, 2024. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1359088/retrieve
-
- Bailey KR, Crawley JN. Anxiety‐related behaviors in mice, in: Buccafusco JJ (ed), Methods of behavior analysis in neuroscience, second ed. : CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Accessed June 3, 2024 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK5221/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

