Roles of long non‑coding RNAs in esophageal cell squamous carcinoma (Review)
- PMID: 38963019
- PMCID: PMC11232667
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5396
Roles of long non‑coding RNAs in esophageal cell squamous carcinoma (Review)
Abstract
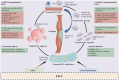
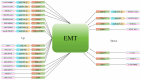
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a prevalent and deadly malignancy of the digestive tract. Recent research has identified long non‑coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as crucial regulators in the pathogenesis of ESCC. These lncRNAs, typically exceeding 200 nucleotides, modulate gene expression through various mechanisms, including the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) pathway and RNA‑protein interactions. The current study reviews the multifaceted roles of lncRNAs in ESCC, highlighting their involvement in processes such as proliferation, migration, invasion, epithelial‑mesenchymal transition, cell cycle progression, resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, glycolysis, apoptosis, angiogenesis, autophagy, tumor growth, metastasis and the maintenance of cancer stem cells. Specific lncRNAs like HLA complex P5, LINC00963 and non‑coding repressor of NFAT have been shown to enhance resistance to radio‑ and chemotherapy by modulating pathways such as AKT signaling and microRNA interaction, which promote cell survival and proliferation under therapeutic stress. Furthermore, lncRNAs like family with sequence similarity 83, member A antisense RNA 1, zinc finger NFX1‑type containing 1 antisense RNA 1 and taurine upregulated gene 1 are implicated in enhancing invasive and proliferative capabilities of ESCC cells through the ceRNA mechanism, while interactions with RNA‑binding proteins further influence cancer cell behavior. The comprehensive analysis underscores the potential of lncRNAs as biomarkers for prognosis and therapeutic targets in ESCC, suggesting avenues for future research focused on elucidating the detailed molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of lncRNAs in ESCC management.
Keywords: epithelial‑mesenchymal transition; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; long non‑coding RNAs; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

