Deciphering the molecular landscape of ionising radiation-induced eye damage with the help of genomic data mining
- PMID: 38963141
- PMCID: PMC11223508
- DOI: 10.2478/aiht-2024-75-3817
Deciphering the molecular landscape of ionising radiation-induced eye damage with the help of genomic data mining
Abstract
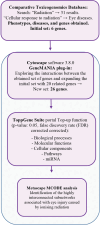
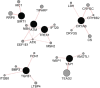
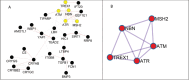
Even at low levels, exposure to ionising radiation can lead to eye damage. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not yet fully understood. We aimed to address this gap with a comprehensive in silico approach to the issue. For this purpose we relied on the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD), ToppGene Suite, Cytoscape, GeneMANIA, and Metascape to identify six key regulator genes associated with radiation-induced eye damage (ATM, CRYAB, SIRT1, TGFB1, TREX1, and YAP1), all of which have physical interactions. Some of the identified molecular functions revolve around DNA repair mechanisms, while others are involved in protein binding, enzymatic activities, metabolic processes, and post-translational protein modifications. The biological processes are mostly centred on response to DNA damage, the p53 signalling pathway in particular. We identified a significant role of several miRNAs, such as hsa-miR-183 and hsamiR-589, in the mechanisms behind ionising radiation-induced eye injuries. Our study offers a valuable method for gaining deeper insights into the adverse effects of radiation exposure.
Izloženost ionizirajućem zračenju čak i pri niskim razinama može pridonijeti nastanku oštećenja oka. Međutim, osnovni molekulski mehanizmi i dalje nisu potpuno razjašnjeni. Cilj našega istraživanja bio je ispuniti tu nedostajuću kariku primjenom sveobuhvatnog in silico pristupa problemu. U tu svrhu, pomoću genomskih baza podataka, portala i poslužitelja (Comparative Toxicogenomics Database, ToppGene Suite portal, Cytoscape, GeneMANIA i Metascape), identificirano je šest ključnih regulacijskih gena koji su povezani s oštećenjem oka prouzročenog ionizirajućim zračenjem (ATM, CRYAB, SIRT1, TGFB1, TREX1 i YAP1) i koji su svi bili u fizičkoj interakciji. Neke od identificiranih molekulskih funkcija odnosile su se na mehanizme popravka oštećenja DNA, a druge su bile uključene u vezanje proteina, enzimsku aktivnost, metaboličke procese i posttranslacijske modifikacije proteina. Biološki procesi uglavnom su bili povezani s odgovorom na oštećenje DNA, pogotovo sa signalnim putem p53. Uočena je i značajna uloga nekoliko miRNA, poput hsa-miR-183 i hsa-miR-589, u mehanizmima povezanima s oštećenjem oka prouzročenog ionizirajućim zračenjem. Osim toga, u ovom je istraživanju opisana korisna metoda za ispitivanje štetnih učinaka izloženosti zračenju.
Keywords: DNA damage; biološki učinci zračenja; data mining; istraživanje podataka; miRNAs; ocular damage; oštećenje DNA; oštećenje oka; radiation health effects.
© 2024 Katarina Baralić et al., published by Sciendo.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Twilight effects of low doses of ionizing radiation on cellular systems: a bird's eye view on current concepts and research.Med Oncol. 2010 Jun;27(2):495-509. doi: 10.1007/s12032-009-9241-9. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19504191 Review.
-
Exposure to low dose ionising radiation: Molecular and clinical consequences.Cancer Lett. 2014 Jul 10;349(1):98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.12.015. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24983100 Review.
-
miR-4796 enhances the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to ionising radiation by impairing the DNA repair pathway.Breast Cancer. 2023 Sep;30(5):691-702. doi: 10.1007/s12282-023-01482-1. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37460775
-
Effect of ionizing radiation in sensory ganglion neurons: organization and dynamics of nuclear compartments of DNA damage/repair and their relationship with transcription and cell cycle.Acta Neuropathol. 2011 Oct;122(4):481-93. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0869-0. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Acta Neuropathol. 2011. PMID: 21915754
-
What mechanisms/processes underlie radiation-induced genomic instability?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Oct;69(20):3351-60. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1148-5. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22955377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tamam N, Salah H, Almogren KS, Mahgoub O, Saeed MK, Abdullah Y, Thanh Tai D, Omer H, Sulieman A, Bradley DA. Evaluation of patients’ and occupational radiation risk dose during conventional and inter ventional radiology procedures. Radiat Phys Chem. 2023;207:110818. doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2023.110818. - DOI
-
- UNSCEAR. 2020/2021 Report Volume I, Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing radiation. [displayed 22 April 2024]. Available at https://www.unscear.org/unscear/en/publications/2020_2021_1.html .
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
