Mass Spectrometric Detection and Differentiation of Enzymatically Active Abrin and Ricin Combined with a Novel Affinity Enrichment Technique
- PMID: 38963334
- PMCID: PMC11256886
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00149
Mass Spectrometric Detection and Differentiation of Enzymatically Active Abrin and Ricin Combined with a Novel Affinity Enrichment Technique
Abstract
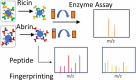
Abrin and ricin are toxic proteins produced by plants. Both proteins are composed of two subunits, an A-chain and a B-chain. The A-chain is responsible for the enzymatic activity, which causes toxicity. The B-chain binds to glycoproteins on the cell surface to direct the A-chain to its target. Both toxins depurinate 28S rRNA, making it impossible to differentiate these toxins based on only their enzymatic activity. We developed an analytical workflow for both ricin and abrin using a single method and sample. We have developed a novel affinity enrichment technique based on the ability of the B-chain to bind a glycoprotein, asialofetuin. After the toxin is extracted with asialofetuin-coated magnetic beads, an RNA substrate is added. Then, depurination is detected by a benchtop matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI TOF) mass spectrometer to determine the presence or absence of an active toxin. Next, the beads are subjected to tryptic digest. Toxin fingerprinting is done on a benchtop MALDI-TOF MS. We validated the assay through sensitivity and specificity studies and determined the limit of detection for each toxin as nanogram level for enzymatic activity and μg level for toxin fingerprinting. We examined potential cross-reactivity from proteins that are near neighbors of the toxins and examined potential false results in the presence of white powders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 3;17(4):177. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040177. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278675 Free PMC article.
-
[Highly toxic type Ⅱ ribosome-inactivating proteins ricin and abrin and their detection methods: a review].Se Pu. 2021 Mar;39(3):260-270. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.10001. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227307 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Detection of ricin activity and structure by using novel galactose-terminated magnetic bead extraction coupled with mass spectrometric detection.Anal Biochem. 2021 Oct 15;631:114364. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2021.114364. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Anal Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34487718 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the variants of the protein toxins ricin and abrin.Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):155-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16618.x. Eur J Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1740126
-
Mass Spectrometric Detection of Bacterial Protein Toxins and Their Enzymatic Activity.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Aug 31;7(9):3497-511. doi: 10.3390/toxins7093497. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26404376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid detection of ricin at trace levels in complex matrices by asialofetuin-coated beads and bottom-up proteomics using high-resolution mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Sep;416(23):5145-5153. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05452-0. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39046503 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 3;17(4):177. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040177. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278675 Free PMC article.
-
Polyclonal antibodies towards abrin and ricin-design and potential application for mass spectrometry-based analysis of human biosamples.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04132-x. Online ahead of print. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40643690
-
Hazardous Materials from Threats to Safety: Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Versatile Safeguarding Platforms.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;16(19):2699. doi: 10.3390/polym16192699. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39408411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U. S. D. o. A . Select Agent and Toxins List. https://www.selectagents.gov/sat/list.htm (accessed on March 22, 2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

