Protamine and Heparin Interactions: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 38963354
- PMCID: PMC11315261
- DOI: 10.4103/aca.aca_117_23
Protamine and Heparin Interactions: A Narrative Review
Abstract
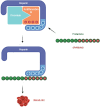
Protamine, first isolated from salmon fish sperm and now produced through recombinant biotechnology, is an antidote that neutralizes the anticoagulant properties of heparin. Protamine function is based on the capacity to dissociate the heparin-antithrombin III (AT III) complex (an important link that promotes blood fluidification by inhibiting coagulation), forming the inactive heparin-protamine complex. Protamine has itself dose-dependent anticoagulant properties: It interferes with coagulation factors and platelet function; it stimulates fibrinolysis; it can lead to thrombocytopenia and reduction in thrombin-related platelet aggregation; it decreases platelet response to thrombin receptor agonist in a dose-dependent manner. In this review, we will focus on protamine and its interaction with heparin. Notably, protamine is able to antagonize not only unfractionated heparin (UFH) but also low molecular weight heparins to various degrees. Protamine-allergic and anaphylactoid systemic reactions may affect up to 1 in 10 people and should be prevented and treated early.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Waldschmidt-Leitz E, Stadler P, Steigerwaldt F. Über blutgerinnung, hemmung und beschleunigung. Z Physik Chem. 1929;183:39.
-
- Levy JH, Faraj BA, Zaidan JR, Camp VM. Effects of protamine on histamine release from human lung. Agents Actions. 1989;28:70–2. - PubMed
-
- Hsu K, Wang D, Shen CY, Chiang CH. Protamine-induced acute lung injury and the protective effect of agents that increase cAMP. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1993;17:57–61. - PubMed
-
- Nybo M, Madsen JS. Serious anaphylactic reactions due to protamine sulfate: A systematic literature review. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;103:192–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

