Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Perioperative Glycemic Control in Adult Diabetic Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery
- PMID: 38963357
- PMCID: PMC11315263
- DOI: 10.4103/aca.aca_209_23
Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Perioperative Glycemic Control in Adult Diabetic Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery
Abstract
Background and objective: To study the effects of dexmedetomidine (DEX) on perioperative blood glucose levels in adult diabetes mellitus (DM) patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
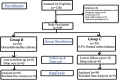
Methods and material: A prospective, observational study was conducted on 100 adult diabetic patients aged between 18 and 75 years undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). The patients were divided into two groups (group D and group C) of 50 each. Group D patients received DEX infusion, whereas the group C patients received 0.9% normal saline infusion.
Results: The blood glucose levels, heart rate, mean arterial pressure, and serum potassium levels at different time points were comparable between the two groups (P > 0.05). The mean dose of insulin required in the combined population as well as in both controlled and uncontrolled DM patients was significantly less in group D than in group C (combined population - 36.03 ± 22.71 vs 47.82 ± 30.19 IU, P = 0.0297; uncontrolled DM - 37.36 ± 23.9 IU vs 48.16 ± 25.15 IU, P = 0.0301; controlled DM - 34.7 ± 21.5 IU vs 47.63 ± 35.25 IU, P = 0.0291). Duration of mechanical ventilation and VIS were comparable between the two groups. The incidence of arrhythmias (20% vs 46%, P = 0.0059) and delirium (6% vs 20%, P = 0.0384) was significantly less in group D than in group C. None of the patients in either group had stroke, myocardial ischemia, and mortality.
Conclusion: The results suggested that DEX infusion during the intraoperative period was very effective for perioperative glycemic control and reduction of insulin requirement in DM patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Outcomes of Cardiac Surgery in Elderly Patients.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016 Dec;30(6):1502-1508. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2016.02.026. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27435836 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of glucose control by added liraglutide to only insulin infusion in diabetic patient undergoing cardiac surgery: A preliminary randomized-controlled trial.Ann Card Anaesth. 2023 Jan-Mar;26(1):63-71. doi: 10.4103/aca.aca_214_20. Ann Card Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 36722590 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardioprotective effects of propofol-dexmedetomidine in open-heart surgery: A prospective double-blind study.Ann Card Anaesth. 2020 Apr-Jun;23(2):134-141. doi: 10.4103/aca.ACA_168_18. Ann Card Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 32275025 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative dexmedetomidine reduces delirium in elderly patients after non-cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials.Can J Anaesth. 2019 Dec;66(12):1489-1500. doi: 10.1007/s12630-019-01440-6. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Can J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31264195 English.
-
Perioperative glycemic control in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2025 Mar;22(1):44-52. doi: 10.5114/kitp.2025.148548. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2025. PMID: 40290708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McAlister FA, Man J, Bistritz L, Amad H, Tandon P. Diabetes and coronary artery bypass surgery. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1518–24. - PubMed
-
- Zhang SJ, Lai G, Griffis CA, Schiltz M, Aroke EN. α2-adrenergic receptor agonist, an attractive but underused ERAS component in improving fast-track recovery and surgical outcomes. AANA J. 2021;89:529–37. - PubMed
-
- Hogan B V, Peter MB, Shenoy HG, Horgan K, Hughes TA. Surgery induced immunosuppression. Surgeon. 2011;9:38–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical