Characteristics of adult retroperitoneal lymphangioma: a single center Chinese cohort study of 15 cases
- PMID: 38963421
- PMCID: PMC11224209
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01143-5
Characteristics of adult retroperitoneal lymphangioma: a single center Chinese cohort study of 15 cases
Abstract
Background: Lymphangioma is a rare cystic tumor that occurs across different locations. Retroperitoneal lymphangioma accounts for about 1% of all lymphangiomas. In this study, we report the clinicopathological features of retroperitoneal lymphangioma and describe our experience in treating this disease.
Methods: We collected clinical data from all patients who were pathologically diagnosed with retroperitoneal lymphangioma at Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, between June 2013 and August 2022.
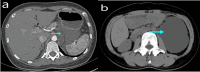
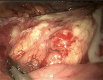
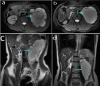
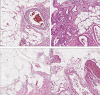
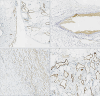
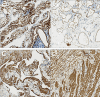
Results: The 7 and 8 male and female patients analyzed herein had a mean age of 48.6 (SD 14.24) years at diagnosis. The mean duration of follow-up was 4.7 years. Among them, 66.67% were asymptomatic, with the rest manifesting abdominal pain, nausea, low back pain and elevated blood pressure as the main symptoms. Preoperative diagnosis and evaluation of cysts were mainly performed via computed tomography (CT) (n = 10, 66.67%) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (n = 8, 53.33%). All patients were completely resected following surgery. Immunohistochemical analysis, performed on 6 patients, revealed that they were positive for D2-40. A total of 4, 4 and 3 patients were positive for CD31, CD34 and SMA, respectively. Moreover, the study cohort had an average postoperative hospital stay of 6.6 days. Follow up, after the end of the study, revealed no relapse in any of the 15 patients.
Conclusions: Lymphangioma is a benign tumor of the lymphatic system. Although typical imaging features can be accurate for preoperative diagnosis, histological examination is crucial to final confirmation. Complete surgical resection is the best option to limit the risk of recurrence in cases with symptomatic lesions.
Keywords: CD34; D2-40; Diagnostic; Prognosis; Retroperitoneal lymphangioma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characteristics of adult abdominal cystic Lymphangioma: a single-center Chinese cohort of 12 cases.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul 29;20(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01388-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32727377 Free PMC article.
-
[Retroperitoneal cystic lymphangioma: about 5 cases and review of the literature].Pan Afr Med J. 2016 Oct 6;25:73. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.25.73.10002. eCollection 2016. Pan Afr Med J. 2016. PMID: 28292036 Free PMC article. Review. French.
-
Intra-abdominal Cystic Lymphangiomas: The Vanderbilt Experience.J Surg Res. 2023 May;285:197-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2022.12.026. Epub 2023 Jan 23. J Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36696706 Review.
-
Retroperitoneal cystic lymphangioma in an adult: A case report and review of the literature.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010 Dec 15;1(5):171-6. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i5.171. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010. PMID: 21607159 Free PMC article.
-
Asymptomatic lymphangioma involving the spleen and retroperitoneum in adults.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Nov 28;15(44):5620-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5620. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19938204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surlin V, Georgescu E, Dumitrescu C, Râmboiu S, Comănescu MV, Ghiluşi M. Retropancreatic cystic lymphangioma—considerations upon a case. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(Suppl):493–496. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
