Chemical composition and studying the possible neuroprotective effect of iridoids-rich fraction from Pentas lanceolata leaves using rotenone model of Parkinson's disease in mice
- PMID: 38963536
- PMCID: PMC11550285
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-024-01509-9
Chemical composition and studying the possible neuroprotective effect of iridoids-rich fraction from Pentas lanceolata leaves using rotenone model of Parkinson's disease in mice
Abstract
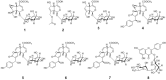
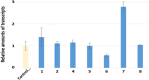
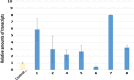
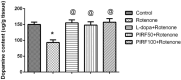
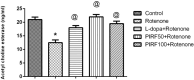
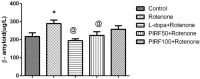
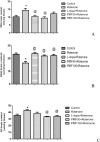
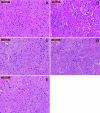
Parkinsonism is an age-related neurodegenerative illness that affects motor coordination leading to loss of dopaminergic neurons. Many medications are used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease but are only symptomatic and have a limited effect on the progression of this ailment. Therefore, bioactive compounds which derived from plants have been examined for their ability to improve the neuronal damage and cell death happened in parkinsonian patients. In this study the iridoids-rich fraction isolated from Pentas lanceolata (PIRF) leaves was investigated for its phytoconstituents. Seven iridoids (1-7) and one flavonol diglycoside (8) were isolated, and their chemical structures were achieved by 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance and ESI-MS spectral data. Compound 1 (6β,7β-epoxy-8-epi-splendoside) and 5 (gaertneroside) were isolated for the first time from Pentas genus as well as compound 8 (kaempferol-3-O-robinobioside). The current study aims to investigate the possible anti-parkinsonian effect of PIRF using a rotenone model of Parkinsonism in mice. Behavioural tests (wirehanging, stair and wooden-walking tests) were done to examine the motor coordination in mice after treatment. Biochemical and histopathological examinations for brain striatum in different groups were also evaluated. Results revealed that rotenone-treated mice had poor motor functions described by depletion of dopamine and Ach levels, a significant increase in proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1B, TNF-α and Mcp-1 and oxidative biomarkers with subsequent reduction in antioxidant mediators. Disorganization of striatum, degenerated neurocytes, slight vacuolation, shrunken neurons with pyknotic nuclei and apoptotic cells are displayed by histopathological examinations. Treatment with PIRF ameliorates the neurodegeneration-induced by rotenone in the brain of mice. The anti-parkinsonian effect of PIRF could be attributed to their bioactive constituents of iridoids.
Keywords: Pentas lanceolata; Behavioral tests Rotenone; Motor functions; Parkinson's disease; Plant iridoids.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Taurine, an essential amino acid, attenuates rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease in rats by inhibiting alpha-synuclein aggregation and augmenting dopamine release.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Mar 5;480:115397. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115397. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39674372
-
Protective effects of evening primrose oil on behavioral activities, nigral microglia and histopathological changes in a rat model of rotenone-induced parkinsonism.J Chem Neuroanat. 2023 Jan;127:102206. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2022.102206. Epub 2022 Dec 1. J Chem Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 36464068
-
Ethnopharmacological validation of Karkataka Taila-An edible crab Rasayana in rotenone-induced in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118691. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118691. Epub 2024 Aug 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39134229
-
The Protective Effect of Korean Red Ginseng Against Rotenone-Induced Parkinson's Disease in Rat Model: Modulation of Nuclear Factor-κβ and Caspase-3.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(7):588-594. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190611122747. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31198107
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Interventions in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 23;45(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01556-y. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40410612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd-Alla HI, Sweelam HTM, Mohamed TA, Gabr MM, El-Safty MM, Hegazy MEF (2017) Efficacy of extracts and iridoid glucosides from Pentas lanceolata on humoral and cell-mediated immune response of viral vaccine. Med Chem Res 26:2196–2204. 10.1007/s00044-017-1935-5
-
- Abd-Alla HI, Kutkat O, Sweelam HT et al (2022) Investigating the potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 and anti-MERS-CoV activities of yellow necklacepod among three selected medicinal plants: Extraction, isolation, identification, in vitro, modes of action, and molecular docking studies. Metabolites 12:1109–1118. 10.3390/metabo12111109 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abd-Alla HI, Saad SA, Shalaby NM, Aly HF, Afify AE, Ali HF, Abdel-Moein NM (2024) A review of iridoid glycosides content and their biological properties from genus Citharexylum. Egypt J Chem 67:756–770. 10.21608/EJCHEM.2024.272834.9391
-
- Abdel-Salam OME, Omara EA, El-Shamarka ME, Hussein JS (2014) Nigrostriatal damage after systemic rotenone and/or lipopolysaccharide and the effect of cannabis. Comp Clin Pathol 23:1343–1358. 10.1007/s00580-013-1788-3
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
