Intraoperative radiotherapy after neurosurgical resection of brain metastases as institutional standard treatment- update of the oncological outcome form a single center cohort after 117 procedures
- PMID: 38963657
- PMCID: PMC11269407
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-024-04691-6
Intraoperative radiotherapy after neurosurgical resection of brain metastases as institutional standard treatment- update of the oncological outcome form a single center cohort after 117 procedures
Abstract
Purpose: Stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) is the predominant method for the irradiation of resection cavities after resection of brain metastases (BM). Intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) with 50 kV x-rays is an alternative way to irradiate the resection cavity focally. We have already reported the outcome of our first 40 IORT patients treated until 2020. Since then, IORT has become the predominant cavity treatment in our center due to patients´ choice.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the outcomes of all patients who underwent resection of BM and IORT between 2013 and August 2023 at Augsburg University Medical Center (UKA).
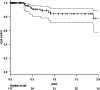
Results: We identified 105 patients with 117 resected BM treated with 50 kV x-ray IORT. Median diameter of the resected metastases was 3.1 cm (range 1.3 - 7.0 cm). Median applied dose was 20 Gy. All patients received standardized follow-up (FU) including three-monthly MRI of the brain. Mean FU was 14 months, with a median MRI FU for patients alive of nine months. Median overall survival (OS) of all treated patients was 18.2 months (estimated 1-year OS 57.7%). The observed local control (LC) rate of the resection cavity was 90.5% (estimated 1-year LC 84.2%). Distant brain control (DC) was 61.9% (estimated 1-year DC 47.9%). Only 16.2% of all patients needed WBI in the further course of disease. The observed radio necrosis rate was 2.6%.
Conclusion: After 117 procedures IORT still appears to be a safe and appealing way to perform cavity RT after neurosurgical resection of BM with low toxicity and excellent LC.
Keywords: Brachytherapy; Brain metastasis; Cavity RT; Focal radiotherapy; IORT.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
KHK has received travel grants and speakers honoria from Varian, Elekta, Zeiss Meditec, AstraZeneca, BMS, MSD, Sanofi-Aventis, Merck and Icotec. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resection with intraoperative radiotherapy vs. adjuvant radiotherapy in the treatment of eloquent brain metastases: an analysis of feasibility and safety.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Apr 24;48(1):385. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03523-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40272585 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative radiotherapy with low-energy x-rays after neurosurgical resection of brain metastases-an Augsburg University Medical Center experience.Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 Dec;197(12):1124-1130. doi: 10.1007/s00066-021-01831-z. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021. PMID: 34415358 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I/II study of resection and intraoperative cesium-131 radioisotope brachytherapy in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases.J Neurosurg. 2014 Aug;121(2):338-48. doi: 10.3171/2014.3.JNS131140. Epub 2014 May 2. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24785322 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of regular magnetic resonance imaging follow-up after stereotactic radiotherapy to the surgical cavity in patients with one to three brain metastases.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Mar 14;14(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1252-x. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30871597 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hypofractionated postoperative stereotactic radiotherapy for large resected brain metastases.Cancer Radiother. 2023 Apr;27(2):87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2022.07.006. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Cancer Radiother. 2023. PMID: 36075831 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HSRT) after brain metastasis surgery: impact on oncological outcome and radionecrosis.J Neurooncol. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s11060-025-05152-4. Online ahead of print. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 40802117
-
Innovation and technology in neurosurgery oncology.J Neurooncol. 2025 May;172(3):499-502. doi: 10.1007/s11060-025-04941-1. Epub 2025 Feb 3. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 39899178 No abstract available.
-
Resection with intraoperative radiotherapy vs. adjuvant radiotherapy in the treatment of eloquent brain metastases: an analysis of feasibility and safety.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Apr 24;48(1):385. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03523-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40272585 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the brain tumor microenvironment by focused ultrasound.Mol Ther Oncol. 2025 May 14;33(2):200994. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2025.200994. eCollection 2025 Jun 18. Mol Ther Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40520576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vogelbaum MA, Brown PD, Messersmith H, Brastianos PK, Burri S, Cahill D, Dunn IF, Gaspar LE, Gatson NTN, Gondi V, Jordan JT, Lassman AB, Maues J, Mohile N, Redjal N, Stevens G, Sulman E, Van Den Bent M, Wallace HJ, Weinberg JS, Zadeh G, Schiff D (2022) Treatment for Brain Metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO Guideline. JCO 40:492–516. 10.1200/JCO.21.0231410.1200/JCO.21.02314 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Le Rhun E, Guckenberger M, Smits M, Dummer R, Bachelot T, Sahm F, Galldiks N, De Azambuja E, Berghoff AS, Metellus P, Peters S, Hong Y-K, Winkler F, Schadendorf D, Van Den Bent M, Seoane J, Stahel R, Minniti G, Wesseling P, Weller M, Preusser M (2021) EANO–ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with brain metastasis from solid tumours. Ann Oncol 32:1332–1347. 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.07.016 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.07.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gutschenritter T, Venur VA, Combs SE, Vellayappan B, Patel AP, Foote M, Redmond KJ, Wang TJC, Sahgal A, Chao ST, Suh JH, Chang EL, Ellenbogen RG, Lo SS (2020) The Judicious Use of Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy in the Management of Large Brain Metastases. Cancers 13:70. 10.3390/cancers13010070 10.3390/cancers13010070 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann R-D, Carrie C, Hassel MB, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller R-P (2011) Adjuvant Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Versus Observation After Radiosurgery or Surgical Resection of One to Three Cerebral Metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952–26001 Study. JCO 29:134–141. 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.165510.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Whitton AC, Greenspoon J, Parney IF, Laack NNI, Ashman JB, Bahary J-P, Hadjipanayis CG, Urbanic JJ, Barker FG, Farace E, Khuntia D, Giannini C, Buckner JC, Galanis E, Roberge D (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1049–1060. 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical