Unlocking the therapeutic potential: odyssey of induced pluripotent stem cells in precision cell therapies
- PMID: 38963728
- PMCID: PMC11487032
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001892
Unlocking the therapeutic potential: odyssey of induced pluripotent stem cells in precision cell therapies
Abstract
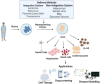
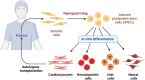
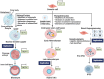
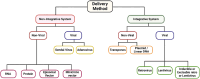
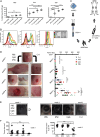
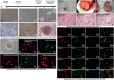
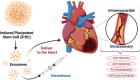
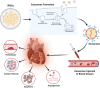
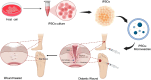
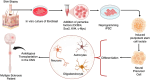
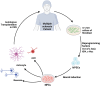
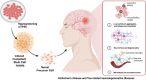
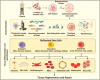
This review explores the application of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in regenerative medicine. The therapeutic significance of iPSC-derived cell therapy within regenerative medicine, emphasizes their reprogramming process and crucial role in cellular differentiation while setting the purpose and scope for the comprehensive exploration of iPSC-derived cell therapy. The subsequent sections intricately examine iPSC-derived cell therapy, unraveling the diverse derivatives of iPSCs and striking a delicate balance between advantages and limitations in therapeutic applications. Mechanisms of action, revealing how iPSC-derived cells seamlessly integrate into tissues, induce regeneration, and contribute to disease modeling and drug screening advancements is discussed. The analysis extends to clinical trials, shedding light on outcomes, safety considerations, and ethical dimensions. Challenges and concerns, including the risk of tumorigenesis and scalability issues, are explored. The focus extends to disease-specific applications, showcasing iPSC-derived cell therapy as a promising avenue for various medical conditions, supported by illustrative case studies. Future directions and research needs are outlined, identifying areas for further exploration, safety considerations and potential enhancements that will shape the future landscape of iPSC-derived therapies. In conclusion, this review provides a significant understanding of iPSC-derived cell therapy's status that contemplates the implications for regenerative medicine and personalized treatment using iPSCs, offering a comprehensive perspective on the evolving field within the confines of a dynamic and promising scientific frontier.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

