CB2 stimulation of adipose resident ILC2s orchestrates immune balance and ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 38963763
- PMCID: PMC11317174
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114434
CB2 stimulation of adipose resident ILC2s orchestrates immune balance and ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
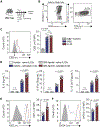
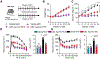
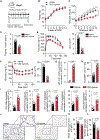
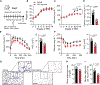
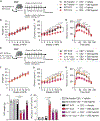
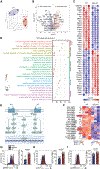
Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with low-grade chronic type 2 inflammation and disturbance of glucose homeostasis. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) play a critical role in maintaining adipose homeostasis via the production of type 2 cytokines. Here, we demonstrate that CB2, a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) and member of the endocannabinoid system, is expressed on both visceral adipose tissue (VAT)-derived murine and human ILC2s. Moreover, we utilize a combination of ex vivo and in vivo approaches to explore the functional and therapeutic impacts of CB2 engagement on VAT ILC2s in a T2DM model. Our results show that CB2 stimulation of ILC2s protects against insulin-resistance onset, ameliorates glucose tolerance, and reverses established insulin resistance. Our mechanistic studies reveal that the therapeutic effects of CB2 are mediated through activation of the AKT, ERK1/2, and CREB pathways on ILC2s. The results reveal that the CB2 agonist can serve as a candidate for the prevention and treatment of T2DM.
Keywords: CB2; CP: Immunology; CP: Metabolism; ILC2; T2DM; adipose inflammation; glucose tolerance; immunotherapy; insulin resistance.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
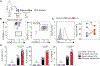
References
-
- Hurrell BP, Sakano Y, Shen S, Helou DG, Li M, Shafiei-Jahani P, Kazemi MH, Sakano K, Li X, Quach C, et al. (2024). Iron controls the development of airway hyperreactivity by regulating ILC2 metabolism and effector function. Sci. Transl. Med. 16, eadk4728. 10.1126/scitranslmed.adk4728. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

