USP9X inhibits metastasis in pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis and immune infiltration
- PMID: 38964032
- PMCID: PMC11283126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.101950
USP9X inhibits metastasis in pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis and immune infiltration
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma (PSC) is a highly invasive pulmonary malignancy with an extremely poor prognosis. The results of previous studies suggest that ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9X (USP9X) contributes to the progression of numerous types of cancer. Nevertheless, there is little knowledge about the molecular mechanisms and functions of USP9X in the metastasis of PSC.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry and western blotting were used to detect USP9X expression levels in PSC tissues and cells. Wound healing, transwell, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), tube formation, and aortic ring assays were used to examine the function and mechanism of USP9X in the metastasis of PSC.
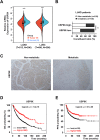
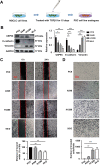
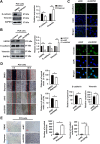
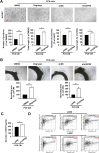
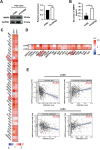
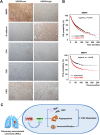
Results: Expression of USP9X was markedly decreased and significantly correlated with metastasis and prognosis of patients with PSC. Then we revealed that USP9X protein levels were negatively associated with the levels of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers and the migration of PSC cells. It was confirmed that USP9X in PSC cells reduced VEGF secretion and inhibited tubule formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in vitro. USP9X was detected to downregulate MMP9. Meanwhile, MMP9 was positively related to EMT, angiogenesis and was negatively related to immune infiltration in the public databases. USP9X was significantly negatively associated with the expression of MMP9, EMT markers, CD31, and positively associated with CD4, and CD8 in PSC tissues.
Conclusion: The present study reveals the vital role of USP9X in regulating EMT, angiogenesis and immune infiltration and inhibiting metastasis of PSC via downregulating MMP9, which provides a new effective therapeutic target for PSC.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; Immune infiltration; Metastasis; Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas; Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9X.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-26b inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting USP9X.BMC Cancer. 2014 Jun 2;14:393. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-393. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24890815 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinase USP9X promotes cell migration, invasion and inhibits apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer.Oncol Rep. 2017 Dec;38(6):3531-3537. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6050. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29130109
-
Down-Regulation of Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 9X Inhibited Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma via ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways.Biol Pharm Bull. 2022;45(9):1283-1290. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b22-00198. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 36047196
-
Biological characteristics and clinical treatment of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 29;13(3):635-653. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-127. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38601447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of USP9X in cellular functions and tumorigenesis (Review).Oncol Lett. 2023 Oct 10;26(6):506. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14093. eCollection 2023 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37920433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Santucci C, Carioli G, Bertuccio P, Malvezzi M, Pastorino U, Boffetta P, Negri E, Bosetti C, La Vecchia C. Progress in cancer mortality, incidence, and survival: a global overview [J] Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2020;29(5):367–381. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Yan B. He S. Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer [J] Biomed. PharmacOther. 2023;169 - PubMed
-
- Manzotti G, Torricelli F, Benedetta D, Lococo F, Sancisi V, Rossi G, Piana S, Ciarrocchi A. An Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transcriptional Switch Triggers Evolution of Pulmonary Sarcomatoid Carcinoma (PSC) and Identifies Dasatinib as New Therapeutic Option [J] Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25(7):2348–2360. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

