A genome-wide CRISPR screen reveals that antagonism of glutamine metabolism sensitizes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to ferroptotic cell death
- PMID: 38964731
- PMCID: PMC12278720
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217089
A genome-wide CRISPR screen reveals that antagonism of glutamine metabolism sensitizes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to ferroptotic cell death
Abstract
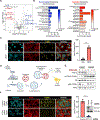
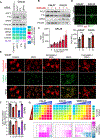
Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid for the growth and survival of rapidly proliferating cancer cells. Many cancers are addicted to glutamine, and as a result, targeting glutamine metabolism has been explored clinically as a therapeutic approach. Glutamine-catalyzing enzymes are highly expressed in primary and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, the nature of the glutamine-associated pathways in this aggressive cancer type has not been elucidated. Here, we explored the therapeutic potential of a broad glutamine antagonist, DRP-104 (sirpiglenastat), in HNSCC tumors and aimed at shedding light on glutamine-dependent pathways in this disease. We observed a potent antitumoral effect of sirpiglenastat in HPV- and HPV + HNSCC xenografts. We conducted a whole-genome CRISPR screen and metabolomics analyses to identify mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to glutamine metabolism blockade. These approaches revealed that glutamine metabolism blockade results in the rapid buildup of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) via autophagy nutrient-sensing pathways. Finally, our analysis demonstrated that GPX4 mediates the protection of HNSCC cells from accumulating toxic lipid peroxides; hence, glutamine blockade sensitizes HNSCC cells to ferroptosis cell death upon GPX4 inhibition. These findings demonstrate the therapeutic potential of sirpiglenastat in HNSCC and establish a novel link between glutamine metabolism and ferroptosis, which may be uniquely translated into targeted glutamine-ferroptosis combination therapies.
Keywords: Autophagy; Ferroptosis; Glutamine; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Poly-unsaturated fatty acids; Precision medicine; Targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Robert Wild and Yumi Yokoyama are stockholders of Dracen Pharmaceuticals. Robert Wild reports consulting fees from Dracen Pharmaceuticals. J. Silvio Gutkind reports consulting fees from Domain Pharmaceuticals, Pangea Therapeutics, and io9 and is the founder of Kadima Pharmaceuticals, all unrelated to the current study. Daniela Nachmanson is an employee of TwinStrand Biosciences. Olivier Harismendy is a current employee and shareholder of Zentalis Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2023, CA Cancer J Clin, 73 (2023) 17–48. - PubMed
-
- Lui VW, Hedberg ML, Li H, Vangara BS, Pendleton K, Zeng Y, Lu Y, Zhang Q, Du Y, Gilbert BR, Freilino M, Sauerwein S, Peyser ND, Xiao D, Diergaarde B, Wang L, Chiosea S, Seethala R, Johnson JT, Kim S, Duvvuri U, Ferris RL, Romkes M, Nukui T, Kwok-Shing Ng P, Garraway LA, Hammerman PS, Mills GB, Grandis JR, Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers, Cancer Discov, 3 (2013) 761–769. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

