Renal autocrine neuropeptide FF (NPFF) signaling regulates blood pressure
- PMID: 38965251
- PMCID: PMC11224344
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-64484-9
Renal autocrine neuropeptide FF (NPFF) signaling regulates blood pressure
Abstract
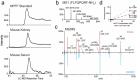
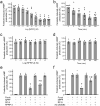
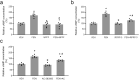
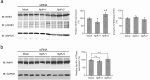
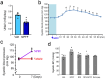
The kidney and brain play critical roles in the regulation of blood pressure. Neuropeptide FF (NPFF), originally isolated from the bovine brain, has been suggested to contribute to the pathogenesis of hypertension. However, the roles of NPFF and its receptors, NPFF-R1 and NPFF-R2, in the regulation of blood pressure, via the kidney, are not known. In this study, we found that the transcripts and proteins of NPFF and its receptors, NPFF-R1 and NPFF-R2, were expressed in mouse and human renal proximal tubules (RPTs). In mouse RPT cells (RPTCs), NPFF, but not RF-amide-related peptide-2 (RFRP-2), decreased the forskolin-stimulated cAMP production in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Furthermore, dopamine D1-like receptors colocalized and co-immunoprecipitated with NPFF-R1 and NPFF-R2 in human RPTCs. The increase in cAMP production in human RPTCs caused by fenoldopam, a D1-like receptor agonist, was attenuated by NPFF, indicating an antagonistic interaction between NPFF and D1-like receptors. The renal subcapsular infusion of NPFF in C57BL/6 mice decreased renal sodium excretion and increased blood pressure. The NPFF-mediated increase in blood pressure was prevented by RF-9, an antagonist of NPFF receptors. Taken together, our findings suggest that autocrine NPFF and its receptors in the kidney regulate blood pressure, but the mechanisms remain to be determined.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Brain; Dopamine D1-like receptor; Kidney; Neuropeptide FF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

