Stem cell therapy in diabetic men with erectile dysfunction: a 24-month follow-up of safety and efficacy of two intracavernous autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells injections, an open label phase 2 clinical trial
- PMID: 38965462
- PMCID: PMC11225209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12610-024-00229-y
Stem cell therapy in diabetic men with erectile dysfunction: a 24-month follow-up of safety and efficacy of two intracavernous autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells injections, an open label phase 2 clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Recently we reported results of phase 1 pilot clinical trial of 2 consecutive intracavernous (IC) injection of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for the first time in the treatment of diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction (DM-ED). In phase 2 of this study our aim is to evaluate long term safety and efficacy of IC injections of BM-MSC on additional eight patients with DM-ED.
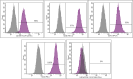
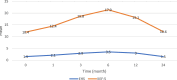
Results: Each patient received 2 consecutive IC injections of BM-MSC and evaluated at 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24-month time points. Primary outcome was the tolerability and safety of stem cells therapy (SCT), while the secondary outcome was improvement of erectile function (EF) as assessed using the International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5), Erection Hardness Score (EHS) questionnaires, and Color Duplex Doppler Ultrasound (CDDU). IC injections of BM-MSCs was safe and well-tolerated. Minor local and short-term adverse events related to the bone marrow aspiration and IC injections were observed and treated conservatively. There were significant improvement in mean IIEF-5, EHS, all over the follow-up time points in comparison to the baseline. At 24-month follow up there were significant decline in the mean IIEF-5, and EHS compared to the baseline. The mean basal and 20-min peak systolic velocity was significantly higher at 3-month after the IC injections compared to baseline.
Conclusions: This phase 2 clinical trial confirmed that IC injections of BM-MSC are safe and improve EF. The decline in EF over time suggests a need for assessing repeated injections.
Clinical trial registration: NCT02945462.
RéSUMé: CONTEXTE: Récemment, nous avons rapporté les résultats d’un essai clinique pilote de phase 1, de 2 injections intracaverneuses (IC) consécutives de cellules souches mésenchymateuses autologues dérivées de la moelle osseuse (BM-MSC), pour la première fois dans le traitement de patients diabétiques atteints de dysfonction érectile (DM-ED). Dans la phase 2 de cette étude, notre objectif est d’évaluer l’innocuité et l’efficacité à long terme des injections IC de BM-MSC sur huit autres patients atteints de dysfonction érectile. RéSULTATS: Chaque patient a reçu 2 injections IC consécutives de BM-MSC, et a été évalué à des intervalles de temps de 1, 3, 6, 12 et 24 mois. Le critère de jugement principal était la tolérance et l’innocuité de la thérapie par cellules souches, tandis que le critère de jugement secondaire était l’amélioration de la fonction érectile (FE) évaluée à l’aide de l’indice international de la fonction érectile-5 (IIEF-5), de questionnaires sur le score de dureté de l’érection (EHS) et de l’échographie Doppler duplex couleur. Les injections IC de BM-MSC se sont avérées sûres et ont été bien tolérées. Des effets indésirables locaux et à court terme mineurs, liés à l’aspiration de la moelle osseuse et aux injections d’IC, ont été observés et traités de manière conservatrice. Il y a eu une amélioration significative des moyennes de l’IIEF-5 moyen, de l’EHS à tous les points de suivi par rapport à la l’état basal. A 24 mois de suivi, il y a eu une baisse significative de l’IIEF-5 moyen et de l’EHS par rapport à l’état basal. La moyenne se base et celle du pic maximal de la vitesse systolique à 20 minutes étaient significativement plus élevées 3 mois après les injections de CI par rapport à l’état de base. CONCLUSIONS: Cet essai clinique de phase 2 a confirmé que les injections de BM-MSC par injections intracaverneuses sont sûres et améliorent la fonction érectile. La baisse de cette dernière au fil du temps suggère une nécessité d’évaluation des injections répétées.
Keywords: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; Diabetic erectile dysfunction; Erectile dysfunction; Stem cells; Stem cells therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Safety and Potential Therapeutic Effect of Two Intracavernous Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells injections in Diabetic Patients with Erectile Dysfunction: An Open Label Phase I Clinical Trial.Urol Int. 2018;101(3):358-365. doi: 10.1159/000492120. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Urol Int. 2018. PMID: 30173210 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and Efficacy of 2 Intracavernous Injections of Allogeneic Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Diabetic Patients with Erectile Dysfunction: Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial.Urol Int. 2021;105(11-12):935-943. doi: 10.1159/000517364. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Urol Int. 2021. PMID: 34384079 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and Potential Effect of a Single Intracavernous Injection of Autologous Adipose-Derived Regenerative Cells in Patients with Erectile Dysfunction Following Radical Prostatectomy: An Open-Label Phase I Clinical Trial.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jan 19;5:204-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.01.024. eCollection 2016 Mar. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27077129 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Treatments of Erectile Dysfunction: Review of the Current Literature.Sex Med Rev. 2021 Jan;9(1):123-132. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2020.03.005. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Sex Med Rev. 2021. PMID: 32631812 Review.
-
Effect of Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave on the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Mens Health. 2019 Mar-Apr;13(2):1557988319846749. doi: 10.1177/1557988319846749. Am J Mens Health. 2019. PMID: 31027441 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effectiveness of electrical stimulation in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Int J Impot Res. 2025 Feb 17. doi: 10.1038/s41443-025-01032-7. Online ahead of print. Int J Impot Res. 2025. PMID: 39962319 Review.
-
Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction: promise or reality? - a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.BMC Urol. 2025 Aug 29;25(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12894-025-01913-5. BMC Urol. 2025. PMID: 40883730 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

