Ultrasound quantification of pleural effusion volume in supine position: comparison of three model formulae
- PMID: 38965488
- PMCID: PMC11225418
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-024-03142-2
Ultrasound quantification of pleural effusion volume in supine position: comparison of three model formulae
Abstract
Background: To investigate the accuracy of three model formulae for ultrasound quantification of pleural effusion (PE) volume in patients in supine position.
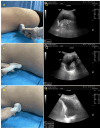
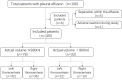
Methods: A prospective study including 100 patients with thoracentesis and drainage of PE was conducted. Three model formulae (single section model, two section model and multi-section model) were used to calculate the PE volume. The correlation and consistency analyses between calculated volumes derived from three models and actual PE volume were performed.
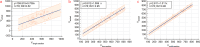
Results: PE volumes calculated by three models all showed significant linear correlations with actual PE volume in supine position (all p < 0.001). The reliability of multi-section model in predicting PE volume was significantly higher than that of single section model and slightly higher than that of two section model. When compared with actual drainage volume, the intra-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) of single section model, two section model and multi-section model were 0.72, 0.97 and 0.99, respectively. Significant consistency between calculated PE volumes by using two section model and multi-section model existed for full PE volume range (ICC 0.98).
Conclusion: Based on the convenience and accuracy of ultrasound quantification of PE volume, two section model is recommended for pleural effusion assessment in routine clinic, though different model formulae can be selected according to clinical needs.
Keywords: Pleural effusion; Quantification; Ultrasound; Volume.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ultrasonographic quantification of pleural effusion: comparison of four formulae.Ultrasonography. 2018 Jul;37(3):254-260. doi: 10.14366/usg.17050. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Ultrasonography. 2018. PMID: 29228764 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of the diagnosis of pleural effusion on supine chest X-ray.Eur Radiol. 1997;7(1):57-60. doi: 10.1007/s003300050109. Eur Radiol. 1997. PMID: 9000398
-
Multiplane ultrasound approach to quantify pleural effusion at the bedside.Intensive Care Med. 2010 Apr;36(4):656-64. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1769-9. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Intensive Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20140421
-
Full head-to-head comparison of ultrasonography and CT scan in volumetric quantification of pleural effusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Emerg Radiol. 2024 Oct;31(5):749-758. doi: 10.1007/s10140-024-02252-y. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Emerg Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38941026
-
Use of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis and treatment of pleural effusion.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Dec;26(23):8771-8776. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202212_30548. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36524495 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

