Exosome for mRNA delivery: strategies and therapeutic applications
- PMID: 38965553
- PMCID: PMC11225225
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02634-x
Exosome for mRNA delivery: strategies and therapeutic applications
Abstract
Messenger RNA (mRNA) has emerged as a promising therapeutic molecule with numerous clinical applications in treating central nervous system disorders, tumors, COVID-19, and other diseases. mRNA therapies must be encapsulated into safe, stable, and effective delivery vehicles to preserve the cargo from degradation and prevent immunogenicity. Exosomes have gained growing attention in mRNA delivery because of their good biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, small size, unique capacity to traverse physiological barriers, and cell-specific tropism. Moreover, these exosomes can be engineered to utilize the natural carriers to target specific cells or tissues. This targeted approach will enhance the efficacy and reduce the side effects of mRNAs. However, difficulties such as a lack of consistent and reliable methods for exosome purification and the efficient encapsulation of large mRNAs into exosomes must be addressed. This article outlines current breakthroughs in cell-derived vesicle-mediated mRNA delivery and its biomedical applications.
Keywords: Exosomes; Targeted delivery; mRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interests.
Figures
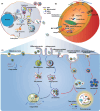
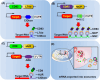
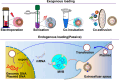
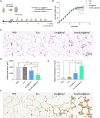
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- QN2022032011L/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China, Project
- 2023A1515011936/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- No. SZGSP013/the Shenzhen Fund for Guangdong Provincial High Level Clinical Key Specialties
- No. SZXK042/the Shenzhen Key Medical Discipline Construction Fund
- XMHT20220104028/the Fund of Development and Reform Commission of Shenzhen Municipality(Shenzhen Engineering Research Center for Precision Psychiatric Technology ).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

