Association between triglyceride-glucose related indices and mortality among individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
- PMID: 38965572
- PMCID: PMC11225330
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02343-7
Association between triglyceride-glucose related indices and mortality among individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of triglyceride-glucose (TyG) related indices in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is still unclear. This study aimed to determine the associations between TyG-related indices and long-term mortality in this population.
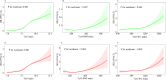
Methods: The data came from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) and National Death Index (NDI). Baseline TyG, TyG combining with body mass index (TyG-BMI), and TyG combining with waist circumference (TyG-WC) indices were calculated, and mortality status was determined through 31 December 2019. Multivariate Cox and restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression models were performed to evaluate the relationship between TyG-related indices and long-term mortality among participants with NAFLD/MASLD. In addition, we examined the association between TyG-related indices and all-cause mortality within subgroups defined by age, sex, race/ethnicity, and fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4).
Results: There were 10,390 participants with completed ultrasonography and laboratory data included in this study. NAFLD was diagnosed in 3672/10,390 (35.3%) participants, while MASLD in 3556/10,390 (34.2%) amongst the overall population. The multivariate Cox regression analyses showed high levels of TyG-related indices, particularly in TyG-BMI and TyG-WC indices were significantly associated with the all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and diabetes mortality in either NAFLD or MASLD. The RCS curves showed a nonlinear trend between three TyG-related indices with all-cause mortality in either NAFLD or MASLD. Subgroup analyses showed that TyG-BMI and TyG-WC indices were more suitable for predicting all-cause mortality in patients without advanced fibrosis.
Conclusion: Our study highlights the clinical value of TyG-related indices in predicting the survival of the NAFLD/MASLD population. TyG-BMI and TyG-WC indices would be the surrogate biomarkers for the follow-up of the population without advanced fibrosis.
Keywords: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Mortality; NHANES III; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; TyG index; TyG-BMI index; TyG-WC index.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

