A novel lncRNA LOC101928222 promotes colorectal cancer angiogenesis by stabilizing HMGCS2 mRNA and increasing cholesterol synthesis
- PMID: 38965575
- PMCID: PMC11223299
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03095-8
A novel lncRNA LOC101928222 promotes colorectal cancer angiogenesis by stabilizing HMGCS2 mRNA and increasing cholesterol synthesis
Abstract
Background: Metastasis is the leading cause of mortality in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and angiogenesis is a crucial factor in tumor invasion and metastasis. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play regulatory functions in various biological processes in tumor cells, however, the roles of lncRNAs in CRC-associated angiogenesis remain to be elucidated in CRC, as do the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: We used bioinformatics to screen differentially expressed lncRNAs from TCGA database. LOC101928222 expression was assessed by qRT-PCR. The impact of LOC101928222 in CRC tumor development was assessed both in vitro and in vivo. The regulatory mechanisms of LOC101928222 in CRC were investigated by cellular fractionation, RNA-sequencing, mass spectrometric, RNA pull-down, RNA immunoprecipitation, RNA stability, and gene-specific m6A assays.
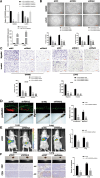
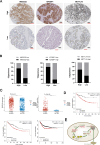
Results: LOC101928222 expression was upregulated in CRC and was correlated with a worse outcome. Moreover, LOC101928222 was shown to promote migration, invasion, and angiogenesis in CRC. Mechanistically, LOC101928222 synergized with IGF2BP1 to stabilize HMGCS2 mRNA through an m6A-dependent pathway, leading to increased cholesterol synthesis and, ultimately, the promotion of CRC development.
Conclusions: In summary, these findings demonstrate a novel, LOC101928222-based mechanism involved in the regulation of cholesterol synthesis and the metastatic potential of CRC. The LOC101928222-HMGCS2-cholesterol synthesis pathway may be an effective target for diagnosing and managing CRC metastasis.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cholesterol synthesis; Colorectal cancer; LOC101928222; m6A.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81972278/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 789ZYRC202090147/789 Outstanding Talent Program of SAHNMU
- LGY2019078/"Six One Project" Top Talent Program for High-level Health Talents in 2019
- JSDW202235/Jiangsu Province Capability Improvement Project through Science, Technology and Education; Jiangsu Provincial Medical Key Discipline Cultivation Unit
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

