Role of endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 38965710
- PMCID: PMC11837575
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2024.023
Role of endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
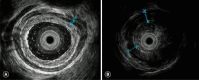
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated disease involving inflammation of the esophagus. Endoscopy is essential in the diagnosis and treatment of EoE and shows typical findings, including esophageal edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and stenosis. However, studies involving pediatric and adult patients with EoE suggest that even a normally appearing esophagus can be diagnosed as EoE by endoscopic biopsy. Therefore, in patients with suspected EoE, biopsy samples should be obtained from the esophagus regardless of endoscopic appearance. Moreover, follow-up endoscopies with biopsy after therapy initiation are usually recommended to assess response. Although previous reports of endoscopic ultrasonography findings in patients with EoE have shown diffuse thickening of the esophageal wall, including lamina propria, submucosa, and muscularis propria, its role in EoE remains uncertain and requires further investigation. Endoscopic dilation or bougienage is a safe and effective procedure that can be used in combination with medical and/or dietary elimination therapy in patients with esophageal stricture for the management of dysphagia and to prevent its recurrence.
Keywords: Endoscopic dilation; Endoscopic ultrasonography; Endoscopy; Eosinophilic esophagitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis: from diagnosis to therapy.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Dec;11(12):1135-1149. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1367664. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28803528 Review.
-
Endoscopic Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Basics and Recent Advances.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;12(12):3202. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123202. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Endoscopy in Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Jan;26(1):187-200. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.08.006. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016. PMID: 26616904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increase in distal esophageal wall thickness with time in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis.JGH Open. 2023 Feb 1;7(3):178-181. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12866. eCollection 2023 Mar. JGH Open. 2023. PMID: 36968573 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: Update in diagnosis and management. Position paper by the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (SIGE).Dig Liver Dis. 2017 Mar;49(3):254-260. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.11.012. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Dig Liver Dis. 2017. PMID: 27979389 Review.
Cited by
-
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Emerging Insights Into Diagnosis and Management.Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2025 Jun;25(2):117-125. doi: 10.7704/kjhugr.2025.0013. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2025. PMID: 40550543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When Manometry and Functional Lumen Imaging Probe Disagree: The Current Limitations of the Chicago Classification Version 4.0 and Probable Extended Indications of Functional Lumen Imaging Probe.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2025 Jul 30;31(3):304-312. doi: 10.5056/jnm25054. Epub 2025 Apr 18. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2025. PMID: 40254534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dynamic Evolution of Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 21;15(3):240. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15030240. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Narrative Review on Diagnosis and Treatment.J Clin Med. 2025 May 27;14(11):3756. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113756. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dellon ES. Eosinophilic esophagitis: what’s in a name? Dig Dis Sci. 2024;69:330–334. - PubMed
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–1363. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

