A Prototype of Graphene E-Nose for Exhaled Breath Detection and Label-Free Diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori Infection
- PMID: 38965802
- PMCID: PMC11425842
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202401695
A Prototype of Graphene E-Nose for Exhaled Breath Detection and Label-Free Diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Abstract
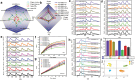
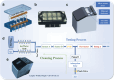
Helicobacter pylori (HP), a common microanaerobic bacteria that lives in the human mouth and stomach, is reported to infect ≈50% of the global population. The current diagnostic methods for HP are either invasive, time-consuming, or harmful. Therefore, a noninvasive and label-free HP diagnostic method needs to be developed urgently. Herein, reduced graphene oxide (rGO) is composited with different metal-based materials to construct a graphene-based electronic nose (e-nose), which exhibits excellent sensitivity and cross-reactive response to several gases in exhaled breath (EB). Principal component analysis (PCA) shows that four typical types of gases in EB can be well discriminated. Additionally, the potential of the e-nose in label-free detection of HP infection is demonstrated through the measurement and analysis of EB samples. Furthermore, a prototype of an e-nose device is designed and constructed for automatic EB detection and HP diagnosis. The accuracy of the prototype machine integrated with the graphene-based e-nose can reach 92% and 91% in the training and validation sets, respectively. These results demonstrate that the highly sensitive graphene-based e-nose has great potential for the label-free diagnosis of HP and may become a novel tool for non-invasive disease screening and diagnosis.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; exhaled breath diagnosis; e‐nose prototype; gas sensors; graphene oxide.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- a) Warren J. R., Lancet 1983, 4, 1273; - PubMed
- b) Warren J. R., Marshall B. J., Lancet 1984, 323, 1311; - PubMed
- c) Liou J.‐M., Fang Y.‐J., Chen C.‐C., Bair M.‐J., Chang C.‐Y., Lee Y.‐C., Chen M.‐J., Chen C.‐C., Tseng C.‐H., Hsu Y.‐C., Lee J.‐Y., Yang T.‐H., Luo J.‐C., Chang C.‐C., Chen C.‐Y., Chen P.‐Y., Shun C.‐T., Hsu W.‐F., Hu W.‐H., Chen Y.‐N., Sheu B.‐S., Lin J.‐T., Wu J.‐Y., El‐Omar E. M., Wu M.‐S., Lancet 2016, 388, 2355; - PubMed
- d) Malfertheiner P., Megraud F., O'Morain C., Bazzoli F., El‐Omar E., Graham D., Hunt R., Rokkas T., Vakil N., Kuipers E. J., Gut 2007, 56, 772; - PMC - PubMed
- e) Zavros Y., Merchant J. L., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 451. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Dinca A. L., Melit L. E., Marginean C. O., Children (Basel) 2022, 9, 1083. - PMC - PubMed
- b) Zheng W., Zhu Z., Ying J., Long G., Chen B., Peng K., Li F., Zhao H., Jiang M., Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 853184; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Thrift A. P., Wenker T. N., El‐Serag H. B., Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 338. - PubMed
-
- a) Hooi J. K. Y., Lai W. Y., Ng W. K., Suen M. M. Y., Underwood F. E., Tanyingoh D., Malfertheiner P., Graham D. Y., Wong V. W. S., Wu J. C. Y., Chan F. K. L., Sung J. J. Y., Kaplan G. G., Ng S. C., Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420; - PubMed
- b) Usarov K., Ahmedov A., Abasiyanik M. F., Ku Khalif K. M. N. i., IIUM Eng. J. 2022, 23, 183;
- c) Thorpe H. A., Tourrette E., Yahara K., Vale F. F., Liu S., Oleastro M., Alarcon T., Perets T. T., Latifi‐Navid S., Yamaoka Y., Martinez‐Gonzalez B., Karayiannis I., Karamitros T., Sgouras D. N., Elamin W., Pascoe B., Sheppard S. K., Ronkainen J., Aro P., Engstrand L., Agreus L., Suerbaum S., Thorell K., Falush D., Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6842. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Malfertheiner P., Megraud F., O'Morain C. A., Atherton J., Axon A. T., Bazzoli F., Gensini G. F., Gisbert J. P., Graham D. Y., Rokkas T., El‐Omar E. M., Kuipers E. J., Gut 2012, 61, 646;
- b) Baral B., Kashyap D., Varshney N., Verma T. P., Jain A. K., Chatterji D., Kumar V., Mishra A., Kumar A., Jha H. C., Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 34. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
