Differences in intestinal and renal Ca and P uptake in three different breeds of growing-finishing pigs
- PMID: 38965863
- PMCID: PMC11229737
- DOI: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2371609
Differences in intestinal and renal Ca and P uptake in three different breeds of growing-finishing pigs
Abstract
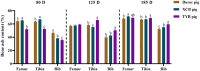
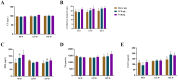
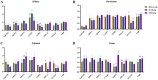
This study investigated the differences in bone growth and turnover and calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P) uptake among three different breeds of growing-finishing pigs. Ninety healthy Duroc, Xiangcun black (XCB), and Taoyuan black (TYB) pigs (30 pigs per breed) at 35 day-old (D) with the average body weight (BW) of their respective breed were assigned and raised to 185 D. The results showed that Duroc pigs had higher bone weight and length than the XCB and TYB pigs at 80, 125, and 185 D and the bone index at 185 D (p < 0.05). Duroc pigs had higher bone mineral densities (femur and tibia) compared with the other two breeds at 80 D and 125 D, whereas TYB pigs had higher mineral content and bone breaking load (rib) compared with the other two breeds at 185 D (p < 0.05). The bone morphogenetic protein-2 and osteocalcin concentrations were higher, and TRACP5b concentration was lower in serum of TYB pigs at 125 D (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, parathyroid hormone, thyroxine, and fibroblast growth factor 23 concentrations were higher in serum of TYB pigs at 185 D (p < 0.05). The TYB pigs had higher apparent total tract digestibility of P at 80 D and 185 D and bone Ca and P contents at 185 D in comparison to the Duroc pigs (p < 0.05). Furthermore, gene expressions related to renal uptake of Ca and P differed among the three breeds of pigs. Collectively, Duroc pigs have higher bone growth, whereas TYB pigs have a higher potential for mineral deposition caused by more active Ca uptake.
Keywords: Breed; bone characteristics; calcium; growing-finishing pigs; phosphorus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential competing interest was reported by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Influence of benzoic acid and phytase in low-phosphorus diets on bone characteristics in growing-finishing pigs.J Anim Sci. 2010 Oct;88(10):3363-71. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-1940. Epub 2010 Jun 18. J Anim Sci. 2010. PMID: 20562353
-
Expressions of Insulin-like Growth Factor System among Different Breeds Impact Piglets' Growth during Weaning.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 25;13(19):3011. doi: 10.3390/ani13193011. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835617 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of porcine sometotropin on calcium and phosphorus balance and markers of bone metabolism in finishing pigs.J Anim Sci. 1999 Aug;77(8):2163-71. doi: 10.2527/1999.7782163x. J Anim Sci. 1999. PMID: 10461995
-
The determination of serum concentrations of osteocalcin in growing pigs and its relationship to end-measures of bone mineralization.J Anim Sci. 1996 Nov;74(11):2719-29. doi: 10.2527/1996.74112719x. J Anim Sci. 1996. PMID: 8923186
-
Review: Aspects of digestibility and requirements for minerals and vitamin D by growing pigs and sows.Animal. 2024 Jun;18 Suppl 1:101125. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2024.101125. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Animal. 2024. PMID: 38575402 Review.
References
-
- AOAC Int . 2019. Official methods of anlaysis of AOAC Int. 21st ed. Rochville (MD): AOAC International.
-
- Bai LL, Wu F, Liu H, Zhang L, Zhang S, Liu L, Piao XS, Liu YH, Thacker PA, Wang FL.. 2017. Effects of dietary calcium levels on growth performance and bone characteristics in pigs in grower-finisher-transitional phase. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 224:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.12.014. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
