OPEN RADICAL CYSTECTOMY: SINGLE CENTER RESULTS AND OUTCOMES IN THE LAST FIVE YEARS
- PMID: 38966027
- PMCID: PMC11221229
- DOI: 10.20471/acc.2023.62.s2.3
OPEN RADICAL CYSTECTOMY: SINGLE CENTER RESULTS AND OUTCOMES IN THE LAST FIVE YEARS
Abstract
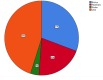
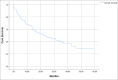
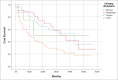
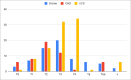
Radical cystectomy is a therapeutic modality of choice for many patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. We conducted a retrospective study of open radical cystectomies performed at a single Center from January 2017 to January 2022. Decision on the urinary diversion type was based on tumor stage, comorbidities, patient age, general condition and preferences. There were 19.5% of female and 80.5% of male patients, median age 67 (range 38-90) years. We performed 96 (44.7%) ureterocutaneostomies (UCS), 67 (31.2%) ileal conduit derivations, and 52 (24.2%) orthotopic neobladder derivations (OND). There were 17 (7.9%) complications after UCS, 7 (3.2%) after incontinent urinary diversion, and 7 (3.2%) after OND. Fifty-five (25.6%) patients developed early complications, of which 31 (14.4%) during the initial hospitalization period, and 24 (11.2%) required re-hospitalization in the 30-day postoperative period. The most common wound-related complication was wound dehiscence, most typically caused by infection. The main reason for readmission was urosepsis. The 30-day mortality rate was 0.9%. Late complications that occurred 30 days after the operation were found in 39 (18.1%) cases. Bladder cancer is a high-mortality disease that requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach. Further development of multidisciplinary teams, perioperative and postoperative care, and follow-up strategy is needed to improve the oncologic and functional outcomes of this procedure.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Cystectomy; Ileal conduit; Survival; Urinary diversion.
Sestre Milosrdnice University Hospital.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and risk factors of 30-day early and 90-day late morbidity and mortality of radical cystectomy during a 13-year follow-up: a comparative propensity-score matched analysis of complications between neobladder and ileal conduit.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014 Jul;44(7):677-85. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyu051. Epub 2014 May 3. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24791782
-
Early and late complications of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: a standardized analysis by urinary diversion type.J Urol. 2014 Mar;191(3):681-7. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.10.022. Epub 2013 Oct 4. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 24099746
-
Comparison of perioperative outcomes and complications of robot assisted radical cystectomy with extracorporeal vs intracorporeal urinary diversion.Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2019 Jul-Aug;43(6):277-283. doi: 10.1016/j.acuro.2019.01.006. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2019. PMID: 31036392 English, Spanish.
-
Urinary diversion after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: options, patient selection, and outcomes.BJU Int. 2014 Jan;113(1):11-23. doi: 10.1111/bju.12121. BJU Int. 2014. PMID: 24330062 Review.
-
Utility of robot-assisted radical cystectomy with intracorporeal urinary diversion for muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Int J Urol. 2019 Mar;26(3):334-340. doi: 10.1111/iju.13900. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Int J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30690817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Veskimäe E, Espinos EL, Bruins HM, Yuan Y, Sylvester R, Kamat AM, et al. What is the prognostic and clinical importance of urothelial and nonurothelial histological variants of bladder cancer in predicting oncological outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer? A European Association of Urology Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer Guidelines Panel Systematic Review. Eur Urol Oncol. 2019;2(6):625–42. 10.1016/j.euo.2019.09.003 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
