Decoding Wilson disease: a machine learning approach to predict neurological symptoms
- PMID: 38966086
- PMCID: PMC11223572
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1418474
Decoding Wilson disease: a machine learning approach to predict neurological symptoms
Abstract
Objectives: Wilson disease (WD) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by a mutation in the ATP7B gene. Neurological symptoms are one of the most common symptoms of WD. This study aims to construct a model that can predict the occurrence of neurological symptoms by combining clinical multidimensional indicators with machine learning methods.
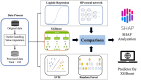
Methods: The study population consisted of WD patients who received treatment at the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from July 2021 to September 2023 and had a Leipzig score ≥ 4 points. Indicators such as general clinical information, imaging, blood and urine tests, and clinical scale measurements were collected from patients, and machine learning methods were employed to construct a prediction model for neurological symptoms. Additionally, the SHAP method was utilized to analyze clinical information to determine which indicators are associated with neurological symptoms.
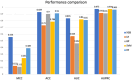
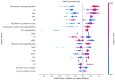
Results: In this study, 185 patients with WD (of whom 163 had neurological symptoms) were analyzed. It was found that using the eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGB) to predict achieved good performance, with an MCC value of 0.556, ACC value of 0.929, AUROC value of 0.835, and AUPRC value of 0.975. Brainstem damage, blood creatinine (Cr), age, indirect bilirubin (IBIL), and ceruloplasmin (CP) were the top five important predictors. Meanwhile, the presence of brainstem damage and the higher the values of Cr, Age, and IBIL, the more likely neurological symptoms were to occur, while the lower the CP value, the more likely neurological symptoms were to occur.
Conclusions: To sum up, the prediction model constructed using machine learning methods to predict WD cirrhosis has high accuracy. The most important indicators in the prediction model were brainstem damage, Cr, age, IBIL, and CP. It provides assistance for clinical decision-making.
Keywords: Wilson disease; eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGB); machine learning; neurological symptom; prediction model.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Wang, Fang, Li, Ding, Song, He, Rao, Diao, Zhu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Application of machine learning model in predicting the likelihood of blood transfusion after hip fracture surgery.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023 Nov;35(11):2643-2656. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02550-4. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023. PMID: 37733228 Clinical Trial.
-
Liver cirrhosis prediction for patients with Wilson disease based on machine learning: a case-control study from southwest China.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Oct 1;34(10):1067-1073. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002424. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35895997 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Blood Transfusion during Cesarean Section and Analysis of Risk Factors of Hypothermia during Anesthesia Recovery.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 13;2022:8661324. doi: 10.1155/2022/8661324. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9863486. doi: 10.1155/2023/9863486. PMID: 35465016 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the R778L Mutation in ATP7B With Wilson Disease in China.Pediatr Neurol. 2023 Aug;145:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2023.04.026. Epub 2023 May 8. Pediatr Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37354629
-
Wilson's Disease: Facing the Challenge of Diagnosing a Rare Disease.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 28;9(9):1100. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091100. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nagral A, Sarma MS, Matthai J, Kukkle PL, Devarbhavi H, Sinha S, et al. . Wilson's Disease: Clinical practice guidelines of the Indian national association for study of the Liver, the Indian society of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition, and the movement disorders society of India. J Clin Exp Hepatol. (2019) 9:74–98. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

