β-Cyclodextrin-based nanoassemblies for the treatment of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38966400
- PMCID: PMC11223813
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbae071
β-Cyclodextrin-based nanoassemblies for the treatment of atherosclerosis
Abstract
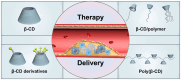
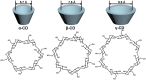
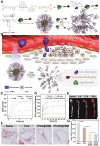
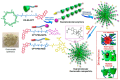
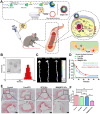
Atherosclerosis, a chronic and progressive condition characterized by the accumulation of inflammatory cells and lipids within artery walls, remains a leading cause of cardiovascular diseases globally. Despite considerable advancements in drug therapeutic strategies aimed at managing atherosclerosis, more effective treatment options for atherosclerosis are still warranted. In this pursuit, the emergence of β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) as a promising therapeutic agent offers a novel therapeutic approach to drug delivery targeting atherosclerosis. The hydrophobic cavity of β-CD facilitates its role as a carrier, enabling the encapsulation and delivery of various therapeutic compounds to affected sites within the vasculature. Notably, β-CD-based nanoassemblies possess the ability to reduce cholesterol levels, mitigate inflammation, solubilize hydrophobic drugs and deliver drugs to affected tissues, making these nanocomponents promising candidates for atherosclerosis management. This review focuses on three major classes of β-CD-based nanoassemblies, including β-CD derivatives-based, β-CD/polymer conjugates-based and polymer β-CD-based nanoassemblies, highlighting a variety of formulations and assembly methods to improve drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy. These β-CD-based nanoassemblies exhibit a variety of therapeutic mechanisms for atherosclerosis and offer systematic strategies for overcoming barriers to drug delivery. Finally, we discuss the present obstacles and potential opportunities in the development and application of β-CD-based nanoassemblies as novel therapeutics for managing atherosclerosis and addressing cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; drug delivery; inflammation; nanoassemblies; β-cyclodextrin.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures





References
-
- Song PG, Fang Z, Wang HY, Cai YT, Rahimi K, Zhu YJ, Fowkes FGR, Fowkes FJ, Rudan I.. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Global Health 2020;8:E721–E29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

