Omega-3 polyunsatured fatty acids and physical performance across the lifespan: a narrative review
- PMID: 38966419
- PMCID: PMC11223594
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1414132
Omega-3 polyunsatured fatty acids and physical performance across the lifespan: a narrative review
Abstract
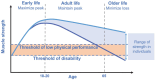
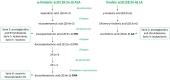
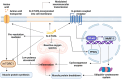
Background and aims: Physical performance is a major contributor of mobility and independence during older life. Despite a progressive decline in musculoskeletal function starts from middle age, several factors acting during the life-course can negatively influence musculoskeletal functional capacities. Lifestyle interventions incorporating nutrition and physical exercise can help maximizing the muscle functional capacities in early life as well as preserving them later in life. Among various dietary compounds, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are gaining growing attention for their potential effects on muscle membrane composition and muscle function. Indeed, several pathways are enhanced, such as an attenuation of pro-inflammatory oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and reduction of insulin resistance.
Methods: We performed a narrative review to explore the existing literature on the relationship between omega-3 PUFAs and physical performance across the life-course.
Results: Growing evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) suggests beneficial effects of omega-3 PUFAs on muscle function, including physical performance parameters in mid to later life. On the other hand, despite a direct association in early life is not available in literature, some mechanisms by which omega-3 PUFAs may contribute to improved adult physical performance could be hypothesized.
Conclusion: Omega-3 PUFAs are gaining growing attention for their positive effect on muscle function parameters. The integration of physical function measures in future studies would be of great interest to explore whether omega-3 PUFAs could contribute to improved muscle function, starting from early life and extending throughout the lifespan. However, larger and high-quality RCTs are needed to fully elucidate the beneficial effects of omega-3 PUFAs supplementation on muscle mass and function.
Keywords: aging; frailty; life course; nutrition; omega-3 PUFAs; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2024 Azzolino, Bertoni, De Cosmi, Spolidoro, Agostoni, Lucchi and Mazzocchi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrition as the foundation for successful aging: a focus on dietary protein and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.Nutr Rev. 2024 Feb 12;82(3):389-406. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad061. Nutr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37319363 Review.
-
Are dietary intake and nutritional status of specific polyunsaturated fatty acids correlated with sarcopenia outcomes in community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia? - Exploratory results from ENHANce.BMC Geriatr. 2023 May 5;23(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04007-9. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37147574 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of long chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on muscle mass and function in sarcopenia: A scoping systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021 Dec;46:73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.10.011. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021. PMID: 34857251
-
The role of omega-3 in the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019 Jun;31(6):825-836. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01146-1. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 30784011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Sarcopenia: Mechanism of Action and Potential Efficacy.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jul 13;21(7):399. doi: 10.3390/md21070399. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37504930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Omega-3 Puzzle: Navigating Challenges and Innovations for Bone Health and Healthy Aging.Mar Drugs. 2024 Sep 28;22(10):446. doi: 10.3390/md22100446. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative balance score and mortality: mediating role of insulin resistance across age strata in the NHANES cohort.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 9;12:1604696. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1604696. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40551744 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional associations between dietary intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids, physical function, and sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults.J Nutr Health Aging. 2025 Jan;29(1):100423. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100423. Epub 2024 Nov 29. J Nutr Health Aging. 2025. PMID: 39615396 Free PMC article.
-
The Oral-Gut Microbiota Axis as a Mediator of Frailty and Sarcopenia.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 23;17(15):2408. doi: 10.3390/nu17152408. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40805993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oral-Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction.Nutrients. 2025 Aug 1;17(15):2538. doi: 10.3390/nu17152538. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

