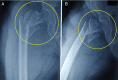
Comparison of Twin Screw Derotation Type Versus Single Helical Blade Type Cephalomedullary Nail in the Management of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures
- PMID: 38966482
- PMCID: PMC11223722
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61638
Comparison of Twin Screw Derotation Type Versus Single Helical Blade Type Cephalomedullary Nail in the Management of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures
Abstract
Background: The intertrochanteric fracture is a frequently occurring fracture, often attributed to osteoporosis in older populations. Recently, there has been a proposal to perform early surgical fixation on elderly patients to facilitate early rehabilitation. This approach has been shown to have a beneficial effect in lowering comorbidities. The study aims to compare the efficacy of the twin screw derotation type cephalomedullary nail with that of the single helical blade type cephalomedullary nail in the management of unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
Methodology: The research sample included patients from the orthopedic outpatient and emergency departments of Adesh Medical College and Hospital, Ambala Cantt, India, who were scheduled for surgery for unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures. The patients were categorized into two groups according to the kind of implant they were given: either a twin screw derotation cephalomedullary nail or a single helical blade cephalomedullary nail. The functional result was evaluated by comparing the modified Harris hip score (HHS). Patients with unstable intertrochanteric fractures, including reverse oblique fractures and fractures with posteromedial comminution, as well as patients who provided consent, were included in this study.
Results: Thirteen individuals received treatment with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA2), whereas 19 individuals received treatment with proximal femoral nail (PFN). The mean age in the PFNA2 group was 69.51, whereas the mean age in the PFN group was 70.804. There were three patients in the PFNA2 group and five patients in the PFN group who had a tip apex distance of more than 25 mm. According to the Cleveland index, nine patients in the PFNA2 group and eight patients in the PFN group had an implant location that was not optimum. Four patients in the PFNA2 group and seven patients in the PFN group had a neck shaft angle difference of more than 10° between their undamaged and operated sides. The mean HHS was 74.55 for the PFNA2 group and 69.88 for the PFN group. The PFNA2 group exhibited four problems, whereas the PFN group had five issues.
Conclusion: The study found that both implants offer similar functional outcomes, with adherence to specific radiological parameters optimizing results. While both face similar challenges with osteoporosis, there was no notable distinction between them. Notably, the PFNA2 group showed superior outcomes in perioperative morbidity.
Keywords: cephalomedullary nail; derotation; implants; intertrochanteric fracture; pfna2; tad.
Copyright © 2024, Thusoo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. The Central Ethical Committee of Adesh Medical College and Hospital, Ambala Cantt issued approval RES/AMC/RAD/2024-5. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of radiological and functional outcome of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures treated using PFN and PFNA-2 in patients with osteoporosis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019 Jul;29(5):1035-1042. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02401-x. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 30778679
-
Surgical and Functional Outcomes of the Results of Conventional Two-Screw Proximal Femoral Nail (PFN) Versus Helical-Blade Anti-rotation Proximal Femoral Nail (PFNA2).Cureus. 2023 Aug 18;15(8):e43698. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43698. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37724213 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Twin Screw Derotation Type Versus Single Helical Blade Type Cephalomedullary Nail in Trochanteric Fractures in Geriatric Population.Cureus. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):e31557. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31557. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36540514 Free PMC article.
-
In reply to the letter to the editor regarding "Comparison of a twin interlocking derotation and compression screw cephalomedullary nail (InterTAN) with a single screw derotation cephalomedullary nail (proximal femoral nail antirotation): a systematic review and meta-analysis for intertrochanteric fractures".J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jul 16;17(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03244-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35842668 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal femoral nailing is superior to hemiarthroplasty in AO/OTA A2 and A3 intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Int Orthop. 2020 Apr;44(4):623-633. doi: 10.1007/s00264-019-04351-9. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Int Orthop. 2020. PMID: 31201487
Cited by
-
How would you like your proximal femoral nail - with a monocortical recon plate, with cable, or neat? A functional and radiological study of reverse oblique (AO/OTA 31-A3) intertrochanteric femur fractures.SICOT J. 2024;10:54. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2024047. Epub 2024 Dec 3. SICOT J. 2024. PMID: 39625218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Comparative study of functional and radiological outcomes of the usage of two devices, derotation type cephalomedullary nail and the helical blade type in unstable intertrochanteric fractures in the geriatric population at a tertiary-level center. Prakash V, Singh N, Gupta GK, Prabhat V. Int J Res Orthop. 2024;10:35–42.
-
- Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:465–475. - PubMed
-
- Timing of surgery for hip fractures in the elderly: a retrospective cohort study. Sasabuchi Y, Matsui H, Lefor AK, Fushimi K, Yasunaga H. Injury. 2018;49:1848–1854. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous