Successful laparoscopic retroperitoneal tumor resection using mixed reality and guiding marker techniques
- PMID: 38966773
- PMCID: PMC11221929
- DOI: 10.1002/iju5.12735
Successful laparoscopic retroperitoneal tumor resection using mixed reality and guiding marker techniques
Abstract
Introduction: Small tumors may be difficult to identify visually and require preoperative effort to locate. Recent advancements in mixed reality technology have improved surgical accuracy in various departments. Here, we present the application of mixed reality-assisted surgery and a guiding marker in the case of small retroperitoneal metastasis of uterine cancer.
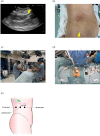
Case presentation: A 67-year-old female with a history of uterine cancer had a retroperitoneal metastasis in the lateroconal fascia near the right diaphragm, measuring 2 cm and infiltrating the peritoneum. We performed precise surgical planning using the preoperative mixed reality software "Holoeyes" on a head-mounted display called HoloLens2. Novel techniques, including ultrasonography-guided placement of a guiding marker and strategic port-site placement facilitated by HoloLens2, ensured accurate tumor identification and laparoscopic resection with minimal blood loss and no intraoperative complications.
Conclusion: The use of mixed reality-assisted surgery and a guiding marker effectively enhanced the precision of retroperitoneal tumor resection.
Keywords: Holoeyes; mixed reality; retroperitoneal.
© 2024 The Author(s). IJU Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Mikio Sugimoto is an Editorial Board member of International Journal of Urology and a co‐author of this article. To minimize bias, they were excluded from all editorial decision‐making related to the acceptance of this article for publication.
Figures


References
-
- Wang L, Zhao Z, Wang G et al. Application of a three‐dimensional visualization model in intraoperative guidance of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Int. J. Urol. 2022; 29: 838–844. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
