Small RNA-mediated genetic switches coordinate ALG-3/4 small RNA pathway function
- PMID: 38967024
- PMCID: PMC11381353
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae586
Small RNA-mediated genetic switches coordinate ALG-3/4 small RNA pathway function
Abstract
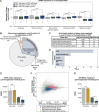
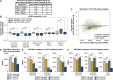
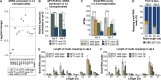
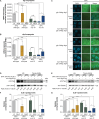
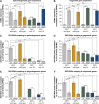
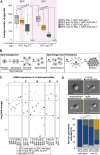
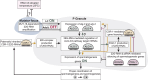
Coordination of gene regulatory networks is necessary for proper execution of cellular programs throughout development. RNA interference (RNAi) is an essential regulatory mechanism in all metazoans. Proper RNAi-mediated gene regulation requires coordination of several RNAi branches to ensure homeostasis. For example, in Caenorhabditis elegans, the Argonautes, ALG-3 and ALG-4, are expressed specifically during spermatogenesis (L4 stage) and bind small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) complementary to sperm-enriched genes. We find that alg-3 and alg-4 are regulated by siRNAs. Our work shows that gene switches are operated via these siRNAs to regulate the Argonautes' expression in a temporal manner. This RNAi-to-RNAi regulatory cascade is essential for coordinating ALG-3/4 pathway function, particularly during heat stress, to provide thermotolerant sperm-based fertility. This work provides insight into one regulatory motif used to maintain RNAi homeostasis, across developmental stages, despite environmental stressors. As RNAi pathways are evolutionarily conserved, other species likely use similar regulatory architectures to maintain RNAi homeostasis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Argonautes ALG-3 and ALG-4 are required for spermatogenesis-specific 26G-RNAs and thermotolerant sperm in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3588-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911685107. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133686 Free PMC article.
-
ALG-5 is a miRNA-associated Argonaute required for proper developmental timing in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 6;45(15):9093-9107. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx536. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28645154 Free PMC article.
-
A low-abundance class of Dicer-dependent siRNAs produced from a variety of features in C. elegans.Genome Res. 2024 Dec 23;34(12):2203-2216. doi: 10.1101/gr.279083.124. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39622635 Free PMC article.
-
Biology and Mechanisms of Short RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Genet. 2013;83:1-69. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407675-4.00001-8. Adv Genet. 2013. PMID: 23890211 Review.
-
Small RNAs, RNAi and the inheritance of gene silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Apr 20;40(4):153-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.12.007. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23618398 Review.
References
-
- Riddle D.L., Blumenthal T., Meyer B.J., Priess J.R.. C. elegans II. 1997; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. - PubMed
-
- Klass M., Wolf N., Hirsh D.. Development of the male reproductive system and sexual transformation in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 1976; 52:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Villeneuve A.M., Meyer B.J.. sdc-1: a link between sex determination and dosage compensation in C. elegans. Cell. 1987; 48:25–37. - PubMed
-
- Miller L.M., Plenefisch J.D., Casson L.P., Meyer B.J.. xol-1: a gene that controls the male modes of both sex determination and X chromosome dosage compensation in C. elegans. Cell. 1988; 55:167–183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

