Hydroxychloroquine attenuates sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in rats
- PMID: 38967533
- PMCID: PMC11331349
- DOI: 10.14744/tjtes.2024.98855
Hydroxychloroquine attenuates sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in rats
Abstract
Background: This study investigates the effects of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) on a sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) model in rats, initiated by a fecal intraperitoneal injection procedure (FIP).
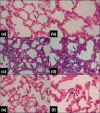
Methods: Three groups were established: control (n=8), FIP + saline (n=7), and FIP + HCQ (20 mg/kg/day) (n=9). Blood samples were collected for arterial blood gas and biochemical analyses, and bilateral pneumonectomy was performed for histopathologic examination.
Results: In the FIP + saline group, PaO2 decreased and PaCO2 increased, whereas these levels normalized in the FIP + HCQ group compared to the control (p<0.001 and p<0.05, respectively). Histopathological scores for alveolar congestion, perivascular/interstitial edema, hemorrhage in alveolar tissue, leukocyte infiltration or aggregation in air spaces/vascular walls, and alveolar wall/hyaline membrane thickness increased in the FIP + saline group compared to the control group (p<0.01). These scores decreased in the FIP + HCQ group compared to the FIP + saline group (p<0.01). HCQ reversed the sepsis-induced increase in malondialdehyde, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and lactic acid.
Conclusion: HCQ may be an effective and safe option to mitigate the severe progression of ARDS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sulfasalazine prevents lung injury due to intra-abdominal sepsis in rats: possible role of Nrf2 and angiopoietin-2.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 May 29;56:e12698. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e12698. eCollection 2023. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 37255096 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of betaine protect against sepsis-induced acute lung injury: CT and histological evidence.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 Nov 13;56:e12906. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e12906. eCollection 2023. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 37970921 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxychloroquine Mitigates Cytokine Storm and Prevents Critical Illness Neuromyopathy in a Rat Sepsis Model.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Nov 1;60(11):1791. doi: 10.3390/medicina60111791. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39596976 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of oxytocin through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant role in a model of sepsis-induced acute lung injury: Demonstrated by CT and histological findings.Exp Lung Res. 2021 Nov;47(9):426-435. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2021.1992808. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Exp Lung Res. 2021. PMID: 34665057
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Sepsis, From Targets to Therapies: A Narrative Review.Anesth Analg. 2020 Nov;131(5):1471-1484. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005146. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 33079870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Fasudil Protects from Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rat via Suppressing STAT-3 and NLRP-3 Pathway.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 May 8;47(5):340. doi: 10.3390/cimb47050340. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gajic O, Dabbagh O, Park PK, Adesanya A, Chang SY, Hou P, et al. U. S. Critical Illness and Injury Trials Group:Lung Injury Prevention Study Investigators (USCIITG-LIPS) Early identification of patients at risk of acute lung injury:evaluation of lung injury prediction score in a multicenter cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:462–70. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stapleton RD, Wang BM, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell ES, Steinberg KP. Causes and timing of death in patients with ARDS. Chest. 2005;128:525–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
