Mixture and Non-mixture Cure Models for Health Technology Assessment: What You Need to Know
- PMID: 38967908
- PMCID: PMC11405446
- DOI: 10.1007/s40273-024-01406-7
Mixture and Non-mixture Cure Models for Health Technology Assessment: What You Need to Know
Abstract
There is increasing interest in the use of cure modelling to inform health technology assessment (HTA) due to the development of new treatments that appear to offer the potential for cure in some patients. However, cure models are often not included in evidence dossiers submitted to HTA agencies, and they are relatively rarely relied upon to inform decision-making. This is likely due to a lack of understanding of how cure models work, what they assume, and how reliable they are. In this tutorial we explain why and when cure models may be useful for HTA, describe the key characteristics of mixture and non-mixture cure models, and demonstrate their use in a range of scenarios, providing Stata code. We highlight key issues that must be taken into account by analysts when fitting these models and by reviewers and decision-makers when interpreting their predictions. In particular, we note that flexible parametric non-mixture cure models have not been used in HTA, but they offer advantages that make them well suited to an HTA context when a cure assumption is valid but follow-up is limited.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.R.L.'s institutions have received consultancy fees and funding, unrelated to the submitted work, from BMS, Merck, Sharpe and Dohme, and from Daiichi Sankyo, GSK, Janssen, Amgen, Sanofi, for projects N.R.L. has worked on.
Figures

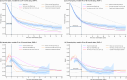
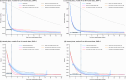

References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. NICE health technology evaluations: the manual. NICE; 2022.
-
- Latimer N. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 14: undertaking survival analysis for economic evaluation alongside clinical trials - Extrapolation with patient-level data. 2011, NICE Decision Support Unit. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

