Nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction by prepectoral implant for the management of giant phyllodes tumors: A case series
- PMID: 38968039
- PMCID: PMC11307034
- DOI: 10.3233/BD-240011
Nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction by prepectoral implant for the management of giant phyllodes tumors: A case series
Abstract
Phyllodes tumor is an uncommon breast neoplasm that is present in variable sizes. Giant phyllodes are those larger than 10 cm in diameter. Clinically, giant phyllodes tumors present as a visible, rapidly growing mass distorting the breast contour. Such tumors with large size and rapid growth rate suggest a phyllode diagnosis of fibroadenoma. Planning a standard treatment strategy for these tumors is quite challenging. While adequate surgical excision with tumor-free resection margins is the standard of care for most giant phyllodes cases, borderline and malignant giant phyllodes tumors might require wider resections given their high recurrence rates. Some authors described total mastectomy as the treatment option for giant borderline and malignant phyllodes to obtain wide, clear margins. Between March 2022 and September 2023, our surgical oncology department presented and operated on three cases of giant phyllodes. They underwent a nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction using pre-pectoral silicone implants. We think that with such a procedure, we can benefit from the wide, safe margins of mastectomy that have been proven to decrease local recurrence rates while considering the aesthetic outcome.
Keywords: Giant phyllodes; breast reconstruction; pre-pectoral implant; recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

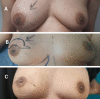
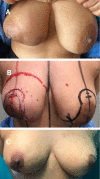
Similar articles
-
The Reconstruction Choice for Giant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: Bi-pedicled Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2017 Aug;41(4):768-772. doi: 10.1007/s00266-017-0792-4. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2017. PMID: 28130560
-
Nipple sparing mastectomy with immediate silicone implant reconstruction for malignant phyllodes tumor in a 19-year-old girl.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Dec;19(23):4498-500. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26698244
-
Immediate implant breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix for treatment of a large recurrent malignant phyllodes tumor.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014 Apr;38(2):373-8. doi: 10.1007/s00266-014-0283-9. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014. PMID: 24570179
-
Recurrent phyllodes tumor of the breast: defining the role for skin-sparing mastectomy and autologous reconstruction.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2011 May;27(4):267-72. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1275493. Epub 2011 Mar 22. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2011. PMID: 21432750 Review.
-
Giant breast tumors: surgical management of phyllodes tumors, potential for reconstructive surgery and a review of literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2008 Nov 11;6:117. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-6-117. World J Surg Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19014438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ye JS, Statistical analysis on the behavior and recurrence of breast phyllodes tumors, J Clin Oncol, 34(3_suppl): e294, 2016. doi:10.1200/jco.2016.34.3_suppl.e294. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

