The association of back pain with physical inactivity and hypothyroidism in pregnant women
- PMID: 38968044
- PMCID: PMC11613002
- DOI: 10.3233/BMR-240086
The association of back pain with physical inactivity and hypothyroidism in pregnant women
Abstract
Background: During pregnancy, structural and functional changes usually occur in the body, which has various consequences, including lower back pain (LBP) and hypothyroidism. One of the risk factors for these problems is physical inactivity.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the association of back pain and physical inactivity, weight gain, and hypothyroidism in pregnant women.
Methods: In this cohort study, 420 pregnant women (26.333 ± 5.820 years old) were included. At first, participants answered this question: "Do you have any plans for pregnancy in the next month?" If the answer was yes, further evaluations were performed. The physical activity and pain intensity were measured by the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-S) and Visual Analogue Scale. Serum TSH was measured by automated chemiluminescence and commercial kits. Measurements were conducted before, the first, second, and third trimester of pregnancy.
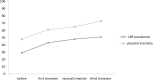
Results: Women reporting LBP were less engaged in physical activities and weight gained in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy was significantly higher than pregnant women without LBP (p< 0.05). TSH level and weight gained in pregnant women with low physical activity level was significantly higher than pregnant women with moderate and high physical activity (p< 0.05) (without significant difference in TSH and BMI). The physical inactivity (before: OR: 1.11 95% CI: 0.89 to 1.22; first trimester: OR: 1.09 95% CI: 1.02 to 1.59; second trimester: OR: 0.92 95% CI: 0.87 to 1.31; third trimester: OR: 1.12 95% CI: 1.02 to 1.39), TSH (OR: 0.85 95% CI: 0.57 to 1.29), and weight gain (second trimester: OR: 0.87 95% CI: 0.92 to 1.59; third trimester: OR: 1.44 95% CI: 1.02 to 1.98; p< 0.05) did predict increased pain intensity.
Conclusion: Using health-oriented approaches to increase physical activity and normalize thyroid function and weight gain during pregnancy can have beneficial effects on LBP.
Keywords: Musculoskeletal disorders; pregnancy; sedentary; thyroid.
Conflict of interest statement
None to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of gestational trimester, physical activity practice and weight gain on the low back and pelvic pain intensity in low risk pregnant women.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019;32(5):671-676. doi: 10.3233/BMR-171006. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31104004 Free PMC article.
-
Low back pain, ultrasonographic muscle thickness measurements and biopsychosocial factors at different trimesters of pregnancy.J Orthop Sci. 2024 Jul;29(4):958-963. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2023.07.006. Epub 2023 Jul 26. J Orthop Sci. 2024. PMID: 37500400
-
Functional changes in back muscle activity correlate with pain intensity and prediction of low back pain during pregnancy.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998 Oct;79(10):1210-2. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90264-7. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998. PMID: 9779673
-
Iron Deficiency May Predict Greater Risk for Hypothyroxinemia: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Pregnant Women in China.Thyroid. 2018 Aug;28(8):968-975. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0491. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Thyroid. 2018. PMID: 29968513
-
[Review of physical exercise as treatment for low back pain in pregnant women].Semergen. 2025 Jan-Feb;51(1):102340. doi: 10.1016/j.semerg.2024.102340. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Semergen. 2025. PMID: 39561422 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Causal relationship between hypothyroidism and peripheral neuropathy: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 27;15:1436823. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1436823. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39665022 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of Sacroiliac Pain: The Current State-of-the-Art.J Pers Med. 2024 Aug 17;14(8):873. doi: 10.3390/jpm14080873. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39202065 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carvalho MECC, Lima LC, Terceiro CAdL, Pinto DRL, Silva MN, Cozer GA, et al. Low back pain during pregnancy. Revista Brasileira De Anestesiologia. 2017; 67: 266-70. - PubMed
-
- Berber MA, Satılmış iG. Characteristics of low back pain in pregnancy, risk factors, and its effects on quality of life. Pain Management Nursing. 2020; 21(6): 579-86. - PubMed
-
- Soldin O, Tractenberg R, Hollowell J, Jonklaas J, Janicic N, Soldin S. Trimester-specific changes in maternal thyroid hormone, thyrotropin, and thyroglobulin concentrations during gestation: trends and associations across trimesters in iodine sufficiency. Thyroid. 2004; 14(12): 1084-90. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Korevaar TI, Medici M, Visser TJ, Peeters RP. Thyroid disease in pregnancy: new insights in diagnosis and clinical management. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2017; 13(10): 610-22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous