Nociceptive Pain in Patients with Neuromuscular Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Clinical Study
- PMID: 38968057
- PMCID: PMC11380240
- DOI: 10.3233/JND-240068
Nociceptive Pain in Patients with Neuromuscular Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Clinical Study
Abstract
Background: Muscle pain is a common symptom in patients with neuromuscular disorders (NMD) and accounts for severely reduced quality of life. OBJECTIVE: This clinical study aimed to observe possible differences in pain prevalence among distinct NMDs and to determine whether the patients' nociceptive pain is influenced by gender, muscle strength and psychological factors and to examine potential pain-associated alterations in muscle properties.
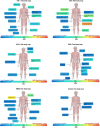
Methods: The cross-sectional study on nociceptive pain in various NMDs involved patient-reported outcomes, muscle strength evaluations (dynamometry and quick motor function test (QMFT)), nociceptive pain evaluations (muscular pressure pain threshold (PPT)), and non-invasive measurement of muscle stiffness, frequency, decrement, relaxation, and creep (myotonometry).
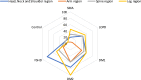
Results: Involving 81 NMD patients and a control group, the study found high variability in pain prevalence among the subgroups. Patients with DM2 and FSHD had significantly higher levels of pain prevalence compared to other examined NMD subgroups and the control group. Female gender, high fatigue levels (representing factors such as depression, anxiety, stress, and impairment of quality of life), and low QMFT scores (representing reduced muscle strength) showed an association with increased sensitivity to pressure pain in the arm and leg region. As assessed by myotonometry, less pain is experienced in neck muscles with a high muscle tone, high stiffness, and a short relaxation time highlighting the importance of intrinsic muscular tone for their pressure pain sensitivity.
Conclusion: Individualized therapeutic concepts including psychological and physical approaches in the pain management of patients with NMDs, especially in women, should be considered. Further research in this field is necessary to gain a more detailed insight into the perception of muscle pain.
Keywords: Nociceptive pain; dynamometry; myotonometry; neuromuscular diseases; pain threshold.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no disclosures regarding this study. Outside of this context, SW has received research grant by the DGM – Deutsche Gesellschaft für Muskelkranke e.V. He has served on advisory boards for Alexion Pharma, CSL Behring and Sanofi Genzyme GmbH. He received funding for travel or speaker Honoraria from Sanofi-Aventis Germany GmbH; SH Glykogenose Gesellschaft; AbbVie Germany GmbH; Recordati Pharma GmbH; CSLBehring GmbH; Alexion Pharma GmbH; Desitin Germany; Akcea GmbH. Outside of this context, BS has served on advisory boards for Alexion, Argenex, Amicus, Astellas, Spark, and Sanofi; he has undertaken contracted unrestricted research for Sanofi and Amicus; and has received honoraria from Kedrion. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

