Experimental study using phantom models of cerebral aneurysms and 4D-DSA to measure blood flow on 3D-color-coded images
- PMID: 38968064
- PMCID: PMC11492053
- DOI: 10.3233/THC-231906
Experimental study using phantom models of cerebral aneurysms and 4D-DSA to measure blood flow on 3D-color-coded images
Abstract
Background: The current 3D-iFlow application can only measure the arrival time of contrast media through intensity values. If the flow rate could be estimated by 3D-iFlow, patient-specific hemodynamics could be determined within the scope of normal diagnostic management, eliminating the need for additional resources for blood flow rate estimation.
Objective: The aim of this study is to develop and validate a method for measuring the flow rate by data obtained from 3D-iFlow images - a prototype application in Four-dimensional digital subtraction angiography (4D-DSA).
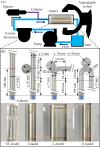
Methods: Using phantom model and experimental circuit with circulating glycerin solution, an equation for the relationship between contrast media intensity and flow rate was developed. Applying the equation to the aneurysm phantom models, the derived flow rate was evaluated.
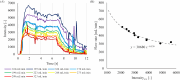
Results: The average errors between the derived flow rate and setting flow rate became larger when the glycerin flow and the X-rays from the X-ray tube of the angiography system were parallel to each other or when the measurement point included overlaps with other contrast enhanced areas.
Conclusion: Although the error increases dependent on the imaging direction and overlap of contrast enhanced area, the developed equation can estimate the flow rate using the image intensity value measured on 3D-iFlow based on 4D-DSA.
Keywords: Aneurysm; four-dimensional digital subtraction angiography; hemodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
K. Otani is a full-time employee of Siemens Healthcare. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures


References
-
- Fujimura S, Yamanaka Y, Takao H, Ishibashi T, Otani K, Karagiozov K, et al. Hemodynamic and morphological differences in cerebral aneurysms between before and after rupture. J Neurosurg. 2023. Sep 1: 1-9. - PubMed
-
- Murayama Y, Fujimura S, Suzuki T, Takao H. Computational fluid dynamics as a risk assessment tool for aneurysm rupture. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. Jul 1; 47(1): E12. - PubMed
-
- Rajabzadeh-Oghaz H, van Ooij P, Veeturi SS, Tutino VM, Zwanenburg JJ, Meng H. Inter-patient variations in flow boundary conditions at middle cerebral artery from 7T PC-MRI and influence on Computational Fluid Dynamics of intracranial aneurysms. Comput Biol Med. 2020. May; 120: 103759. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

