Protocol for adeno-associated virus-mediated optogenetic activation of olfactory output neurons in neonatal mice
- PMID: 38968078
- PMCID: PMC11452914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.103164
Protocol for adeno-associated virus-mediated optogenetic activation of olfactory output neurons in neonatal mice
Abstract
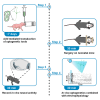
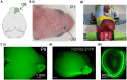
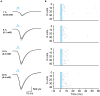
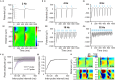
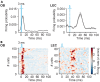
Optogenetic manipulation has proven a powerful tool for investigating the mechanisms underlying the function of neuronal networks, but implementing the technique on mammals during early development remains challenging. Here, we present a comprehensive workflow to specifically manipulate mitral/tufted cells (M/TCs), the output neurons in the olfactory circuit, mediated by adeno-associated virus (AAV) transduction and light stimulation in neonatal mice and monitor neuronal and network activity with in vivo electrophysiology. This method represents an efficient approach to elucidate functional brain development. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Chen et al.1,2,3.
Keywords: biophysics; developmental biology; neuroscience; systems biology.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gretenkord S., Kostka J.K., Hartung H., Watznauer K., Fleck D., Minier-Toribio A., Spehr M., Hanganu-Opatz I.L. Coordinated electrical activity in the olfactory bulb gates the oscillatory entrainment of entorhinal networks in neonatal mice. PLoS Biol. 2019;17 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

