Hospital services utilisation and cost before and after COVID-19 hospital treatment: Evidence from Indonesia
- PMID: 38968247
- PMCID: PMC11226039
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305835
Hospital services utilisation and cost before and after COVID-19 hospital treatment: Evidence from Indonesia
Abstract
Objective: To estimate hospital services utilisation and cost among the Indonesian population enrolled in the National Health Insurance (NHI) program before and after COVID-19 hospital treatment.
Methods: 28,159 Indonesian NHI enrolees treated with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in hospitals between May and August 2020 were compared to 8,995 individuals never diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2020. A difference-in-difference approach is used to contrast the monthly all-cause utilisation rate and total claims of hospital services between these two groups. A period of nine months before and three to six months after hospital treatment were included in the analysis.
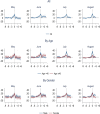
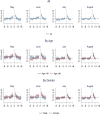
Results: A substantial short-term increase in hospital services utilisation and cost before and after COVID-19 treatment was observed. Using the fifth month before treatment as the reference period, we observed an increased outpatient visits rate in 1-3 calendar months before and up to 2-4 months after treatment (p<0.001) among the COVID-19 group compared to the comparison group. We also found a higher admissions rate in 1-2 months before and one month after treatment (p<0.001). Consequently, increased hospital costs were observed in 1-3 calendar months before and 1-4 calendar months after the treatment (p<0.001). The elevated hospital resource utilisation was more prominent among individuals older than 40. Overall, no substantial increase in hospital outpatient visits, admissions, and costs beyond four months after and five months before COVID-19 treatment.
Conclusion: Individuals with COVID-19 who required hospital treatment had considerably higher healthcare resource utilisation in the short-term, before and after the treatment. These findings indicated that the total cost of treating COVID-19 patients might include the pre- and post-acute period.
Copyright: © 2024 Rizal et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Aleem A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL); 2023. - PubMed
-
- Surendra H, Elyazar IR, Djaafara BA, Ekawati LL, Saraswati K, Adrian V, et al.. Clinical characteristics and mortality associated with COVID-19 in Jakarta, Indonesia: A hospital-based retrospective cohort study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021;9:100108. Epub 2021/03/09. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100108 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Surendra H, Paramita D, Arista NN, Putri AI, Siregar AA, Puspaningrum E, et al.. Geographical variations and district-level factors associated with COVID-19 mortality in Indonesia: a nationwide ecological study. BMC Public Health. 2023;23(1):103. Epub 2023/01/15. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15015-0 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

