Phase separation of RNF214 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38969650
- PMCID: PMC11226663
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06869-2
Phase separation of RNF214 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
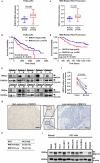
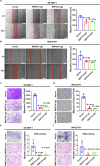
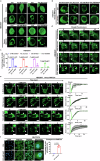
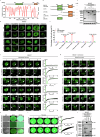
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors, and the expression and function of an uncharacterized protein RNF214 in HCC are still unknown. Phase separation has recently been observed to participate in the progression of HCC. In this study, we investigated the expression, function, and phase separation of RNF214 in HCC. We found that RNF214 was highly expressed in HCC and associated with poor prognosis. RNF214 functioned as an oncogene to promote the proliferation, migration, and metastasis of HCC. Mechanically, RNF214 underwent phase separation, and the coiled-coil (CC) domain of RNF214 mediated its phase separation. Furthermore, the CC domain was necessary for the oncogenic function of RNF214 in HCC. Taken together, our data favored that phase separation of RNF214 promoted the progression of HCC. RNF214 may be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The RNF214-TEAD-YAP signaling axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via TEAD ubiquitylation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 11;15(1):4995. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49045-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38862474 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM65 triggers β-catenin signaling via ubiquitylation of Axin1 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Sci. 2017 Sep 15;130(18):3108-3115. doi: 10.1242/jcs.206623. Epub 2017 Jul 28. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28754688
-
Hypoxia-induced DTL promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma through ubiquitin-mediated degradation of SLTM and subsequent Notch pathway activation.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Oct 9;15(10):734. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07089-4. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39384740 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death 10 promotes metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via PP2Ac-mediated YAP activation.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Sep 14;12(9):849. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04139-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34521817 Free PMC article.
-
Increased long noncoding RNA LASP1-AS is critical for hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis via upregulating LASP1.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):13493-13509. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28028. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30677131
Cited by
-
Targeting phase separation: a promising treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Sep 1;23(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02406-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40890761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membraneless Organelles and Phase Separation in Tumours: Mechanisms and Prospects.Cell Prolif. 2025 Aug;58(8):e70027. doi: 10.1111/cpr.70027. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Cell Prolif. 2025. PMID: 40211955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of liquid-liquid phase separation in liver innate immunity.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 3;22(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01787-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39227829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

