Synthetic extremophiles via species-specific formulations improve microbial therapeutics
- PMID: 38969782
- PMCID: PMC11840811
- DOI: 10.1038/s41563-024-01937-6
Synthetic extremophiles via species-specific formulations improve microbial therapeutics
Abstract
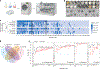
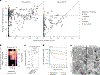
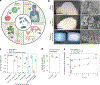
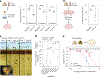
Microorganisms typically used to produce food and pharmaceuticals are now being explored as medicines and agricultural supplements. However, maintaining high viability from manufacturing until use remains an important challenge, requiring sophisticated cold chains and packaging. Here we report synthetic extremophiles of industrially relevant gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli Nissle 1917, Ensifer meliloti), gram-positive bacteria (Lactobacillus plantarum) and yeast (Saccharomyces boulardii). We develop a high-throughput pipeline to define species-specific materials that enable survival through drying, elevated temperatures, organic solvents and ionizing radiation. Using this pipeline, we enhance the stability of E. coli Nissle 1917 by more than four orders of magnitude over commercial formulations and demonstrate its capacity to remain viable while undergoing tableting and pharmaceutical processing. We further show, in live animals and plants, that synthetic extremophiles remain functional against enteric pathogens and as nitrogen-fixing plant supplements even after exposure to elevated temperatures. This synthetic, material-based stabilization enhances our capacity to apply microorganisms in extreme environments on Earth and potentially during exploratory space travel.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
M.J., G.T., J.L. and E.K. are co-inventors on patent application 18/477,970 (filed 29 September 2023 by MIT), which describes the microbial-stabilizing materials and processes reported here. M.J. and G.T. consult for VitaKey. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ozdemir T, Fedorec AJH, Danino T & Barnes CP Synthetic biology and engineered live biotherapeutics: toward increasing system complexity. Cell Syst. 7, 5–16 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Arif I, Batool M & Schenk PM Plant microbiome engineering: expected benefits for improved crop growth and resilience. Trends Biotechnol. 38, 1385–1396 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

