Biocompatibility, bioactivity and immunomodulatory properties of three calcium silicate-based sealers: an in vitro study on hPDLSCs
- PMID: 38969964
- PMCID: PMC11226489
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-024-05812-1
Biocompatibility, bioactivity and immunomodulatory properties of three calcium silicate-based sealers: an in vitro study on hPDLSCs
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the biocompatibility, bioactivity, and immunomodulatory properties of three new calcium silicate cement-based sealers: Ceraseal (CS), Totalfill BC Sealer (TFbc) and WellRoot ST (WR-ST) on human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs).
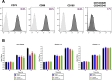
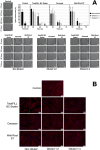
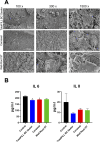
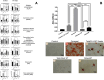
Materials and methods: HPDLSCs were isolated from extracted third molars from healthy patients. Eluates (1:1, 1:2, and 1:4 ratio) and sample discs of CS, TFbc and WR-ST after setting were prepared. A series of assays were performed: cell characterization, cell metabolic activity (MTT assay) cell attachment and morphology (SEM assay), cell migration (wound-healing assay), cytoskeleton organization (phaloidin-based assay); IL-6 and IL-8 release (ELISA); differentiation marker expression (RT-qPCR assay), and cell mineralization (Alizarin Red S staining). HPDLSCs cultured in unconditioned (negative control) or osteogenic (positive control) culture media were used as a comparison. Statistical significance was established at p < 0.05.
Results: All the tested sealers exhibited similar results in the cytocompatibility assays (cell metabolic activity, migration, attachment, morphology, and cytoskeleton organization) compared with a negative control group. CS and TFbc exhibited an upregulation of at least one osteo/cementogenic marker compared to the negative and positive control groups. CS and TFbc also showed a significantly higher calcified nodule formation than the negative and positive control groups. Both the marker expression and calcified nodule formation were significantly higher in CS-treated cells than TFbc treated cells. WR-ST exhibited similar results to the control group. CS and TFbc-treated cells exhibited a significant downregulation of IL-6 after 72 h of culture compared to the negative control group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: All the tested sealers exhibited an adequate cytocompatibility. CS significantly enhances cell differentiation by upregulating the expression of key genes associated with bone and cementum formation. Additionally, CS was observed to facilitate the mineralization of the extracellular matrix effectively. In contrast, the effects of TFbc and WR-ST on these processes were less pronounced compared to CS. Furthermore, both CS and TFbc exhibited an anti-inflammatory potential, contributing to their potential therapeutic benefits in regenerative endodontics.
Clinical relevance: This is the first study to compare the biological properties and immunomodulatory potential of Ceraseal, Totalfill BC Sealer, and WellRoot ST. The results act as supporting evidence for their use in root canal treatment.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Bioacompatibility; Bioactivity; Ceraseal; Totalfill BC sealer; WellRoot ST.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Premixed calcium silicate-based ceramic sealers promote osteogenic/cementogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells: A microscopy study.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Jul;87(7):1584-1597. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24545. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 38433562
-
Comparative bioactivity and immunomodulatory potential of the new Bioroot Flow and AH Plus Bioceramic sealer: An in vitro study on hPDLSCs.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Mar 5;28(3):195. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05593-7. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38441709 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of cytocompatibility of calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers and their effects on the biological responses of mesenchymal dental stem cells.Int Endod J. 2017 Jan;50(1):67-76. doi: 10.1111/iej.12596. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Int Endod J. 2017. PMID: 26660310
-
Tricalcium silicate cement sealers: Do the potential benefits of bioactivity justify the drawbacks?J Am Dent Assoc. 2022 Aug;153(8):750-760. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Mar 5. J Am Dent Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35260235 Review.
-
Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;12(11):1853. doi: 10.3390/life12111853. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36430988 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations-A Review.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;13(4):157. doi: 10.3390/dj13040157. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40277487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Root canal cleanliness and debris extrusion following retreatment of thermoplastic injection technique and bioceramic-based root canal sealer.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Oct 23;28(11):608. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-06005-6. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 39438302
-
Effects of 0.01 mM strontium on human periodontal ligament stem cell osteogenic differentiation via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Int Med Res. 2025 Feb;53(2):3000605251315024. doi: 10.1177/03000605251315024. J Int Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39932304 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Bio MTA plus & ProRoot MTA pulp capping materials on the regenerative properties of human dental pulp stem cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 8;15(1):4749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88816-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39922901 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of different capping materials extracts on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of cultured human dental pulp stem cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 1;15(1):11140. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93759-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40169700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang F, Zhang R, Xu J, Du J, Leng S, Zhang L et al (2022) Comparative effects of concentrated growth factors on the Biological Characteristics of Periodontal Ligament Cells and stem cells from Apical Papilla. J Endod 48(8):1029–1037. 10.1016/j.joen.2022.05.001 10.1016/j.joen.2022.05.001 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

