Deepvirusclassifier: a deep learning tool for classifying SARS-CoV-2 based on viral subtypes within the coronaviridae family
- PMID: 38969970
- PMCID: PMC11225326
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-024-05754-1
Deepvirusclassifier: a deep learning tool for classifying SARS-CoV-2 based on viral subtypes within the coronaviridae family
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we present DeepVirusClassifier, a tool capable of accurately classifying Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral sequences among other subtypes of the coronaviridae family. This classification is achieved through a deep neural network model that relies on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Since viruses within the same family share similar genetic and structural characteristics, the classification process becomes more challenging, necessitating more robust models. With the rapid evolution of viral genomes and the increasing need for timely classification, we aimed to provide a robust and efficient tool that could increase the accuracy of viral identification and classification processes. Contribute to advancing research in viral genomics and assist in surveilling emerging viral strains.
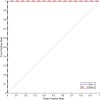
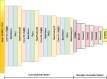
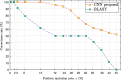
Methods: Based on a one-dimensional deep CNN, the proposed tool is capable of training and testing on the Coronaviridae family, including SARS-CoV-2. Our model's performance was assessed using various metrics, including F1-score and AUROC. Additionally, artificial mutation tests were conducted to evaluate the model's generalization ability across sequence variations. We also used the BLAST algorithm and conducted comprehensive processing time analyses for comparison.
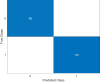
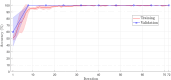
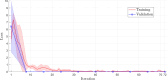
Results: DeepVirusClassifier demonstrated exceptional performance across several evaluation metrics in the training and testing phases. Indicating its robust learning capacity. Notably, during testing on more than 10,000 viral sequences, the model exhibited a more than 99% sensitivity for sequences with fewer than 2000 mutations. The tool achieves superior accuracy and significantly reduced processing times compared to the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool algorithm. Furthermore, the results appear more reliable than the work discussed in the text, indicating that the tool has great potential to revolutionize viral genomic research.
Conclusion: DeepVirusClassifier is a powerful tool for accurately classifying viral sequences, specifically focusing on SARS-CoV-2 and other subtypes within the Coronaviridae family. The superiority of our model becomes evident through rigorous evaluation and comparison with existing methods. Introducing artificial mutations into the sequences demonstrates the tool's ability to identify variations and significantly contributes to viral classification and genomic research. As viral surveillance becomes increasingly critical, our model holds promise in aiding rapid and accurate identification of emerging viral strains.
Keywords: Coronaviridae; Deep learning; SARS-CoV-2; Viral classification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interest is declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zoonotic evolution and implications of microbiome in viral transmission and infection.Virus Res. 2020 Dec;290:198175. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198175. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 33007342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate and fast clade assignment via deep learning and frequency chaos game representation.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 28;12:giac119. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giac119. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 36576129 Free PMC article.
-
New proposal of viral genome representation applied in the classification of SARS-CoV-2 with deep learning.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 11;24(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05188-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36906520 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of SARS-CoV-2 viral genome sequences using Neurochaos Learning.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 Aug;60(8):2245-2255. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02591-3. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022. PMID: 35668230 Free PMC article.
-
Ecology, evolution and classification of bat coronaviruses in the aftermath of SARS.Antiviral Res. 2014 Jan;101:45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.10.013. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24184128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PRCFX-DT: a new graph-based approach for feature selection and classification of genomic sequences.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jun 17;26(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06183-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40528202 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in the development of vaccines and immunotherapeutics-yesterday, today, and tomorrow.Front Artif Intell. 2025 Jul 18;8:1620572. doi: 10.3389/frai.2025.1620572. eCollection 2025. Front Artif Intell. 2025. PMID: 40756816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maghdid HS, Ghafoor KZ, Sadiq AS, Curran K, Rabie K. A novel AI-enabled framework to diagnose coronavirus COVID 19 using smartphone embedded sensors: design study; 2020. arXiv:2003.07434.
-
- Chowdhury MEH, et al. Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia? IEEE Access. 2020;8:132665–132676. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010287. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

