Unraveling the genomic secrets of Tritonibacter mobilis AK171: a plant growth-promoting bacterium isolated from Avicennia marina
- PMID: 38969999
- PMCID: PMC11225332
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10555-0
Unraveling the genomic secrets of Tritonibacter mobilis AK171: a plant growth-promoting bacterium isolated from Avicennia marina
Abstract
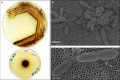
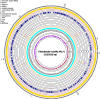
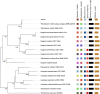
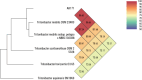
The scarcity of freshwater resources resulting in a significant yield loss presents a pressing challenge in agriculture. To address this issue, utilizing abundantly available saline water could offer a smart solution. In this study, we demonstrate that the genome sequence rhizosphere bacterium Tritonibacter mobilis AK171, a halophilic marine bacterium recognized for its ability to thrive in saline and waterlogged environments, isolated from mangroves, has the remarkable ability to enable plant growth using saline irrigation. AK171 is characterized as rod-shaped cells, displays agile movement in free-living conditions, and adopts a rosette arrangement in static media. Moreover, The qualitative evaluation of PGP traits showed that AK171 could produce siderophores and IAA but could not solubilize phosphate nor produce hydrolytic enzymes it exhibits a remarkable tolerance to high temperatures and salinity. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive genome sequence analysis of T. mobilis AK171 to unravel the genetic mechanisms underlying its plant growth-promoting abilities in such challenging conditions. Our analysis revealed diverse genes and pathways involved in the bacterium's adaptation to salinity and waterlogging stress. Notably, T. mobilis AK171 exhibited a high level of tolerance to salinity and waterlogging through the activation of stress-responsive genes and the production of specific enzymes and metabolites. Additionally, we identified genes associated with biofilm formation, indicating its potential role in establishing symbiotic relationships with host plants. Furthermore, our analysis unveiled the presence of genes responsible for synthesizing antimicrobial compounds, including tropodithietic acid (TDA), which can effectively control phytopathogens. This genomic insight into T. mobilis AK171 provides valuable information for understanding the molecular basis of plant-microbial interactions in saline and waterlogged environments. It offers potential applications for sustainable agriculture in challenging conditions.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Metabolites; Biocontrol; Mangrove; Red sea; Salinity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Salinity on Assembly Characteristics and Function of Microbial Communities in the Phyllosphere and Rhizosphere of Salt-Tolerant Avicennia marina Mangrove Species.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 6;11(2):e0300022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03000-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36744884 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence analysis of plant growth-promoting bacterium, Isoptericola sp. AK164 isolated from the rhizosphere of Avicennia marina growing at the Red Sea coast.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Aug 14;205(9):307. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03654-1. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37580455 Free PMC article.
-
Tapping into haloalkaliphilic bacteria for sustainable agriculture in treated wastewater: insights into genomic fitness and environmental adaptation.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024 Sep 13;118(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s10482-024-02012-5. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024. PMID: 39269515
-
Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Biological Tools for the Mitigation of Salinity Stress in Plants.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jul 7;11:1216. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01216. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32733391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Jul 30;156:225-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 29554608 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the bacterial diversity and potential of the Avicennia marina ecosystem for enhancing plant resilience to saline conditions.Environ Microbiome. 2024 Dec 4;19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s40793-024-00642-w. Environ Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39633419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boukhatem ZF, Merabet C, Tsaki H. Plant Growth promoting Actinobacteria, the most promising candidates as Bioinoculants? Front Agron 2022, 4.
-
- Gong Y, Bai J-L, Yang H-T, Zhang W-D, Xiong Y-W, Ding P, Qin S. Phylogenetic diversity and investigation of plant growth-promoting traits of actinobacteria in coastal salt marsh plant rhizospheres from Jiangsu, China. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2018;41(5):516–27. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.06.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Zelicourt A, Synek L, Saad MM, Alzubaidy H, Jalal R, Xie Y, Andres-Barrao C, Rolli E, Guerard F, Mariappan KG, et al. Ethylene induced plant stress tolerance by Enterobacter sp. SA187 is mediated by 2-keto-4-methylthiobutyric acid production. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(3):e1007273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007273. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

